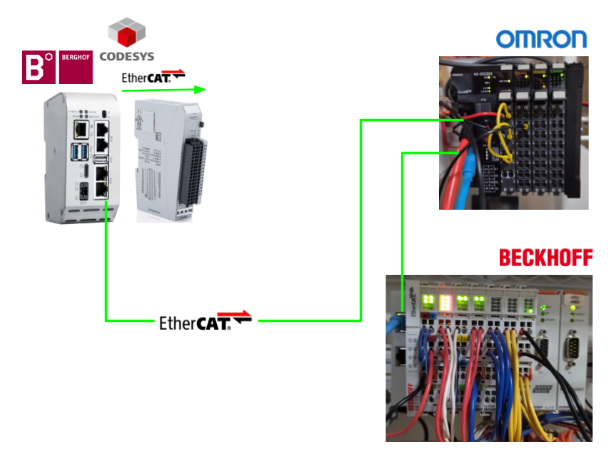
Here is the fourth episode of the introduction of BERGHOF’s Raspberry Pi-based modular CODESYS PLC. This time the EtherCAT Master is set up to communicate locally with the E-IO XR02 from EBUS Communications, as well as with OMRON and Beckhoff’s Coupler.
Thank you for the equipment from BERGHOF.
Come on, let’s enjoy FA.
Reference Link
Implementation1
BERGHOF’s MC-PI controller has three Ethernet interfaces. Note that the second one is EBUS.
There is such a protective COVER.
BERGHOF Side
First it communicates via EBUS with the MC-Pi controller from BERGHOF and the MC-I/O XR series installed next to it.
Configure Network via Web server
Go to the Web Server of BERGHOF’s MC-Pi controller and click Configuration>Network.
Set the Mode of ETH1 to EtherCAT mode.
MC-I/O XR?
MC-I/O is an I/O module system for connecting process signals to any EtherCAT network station. MC-I/O consists of an MC-I/O bus coupler and various MC-I/O modules; the MC-I/O bus coupler converts the physical transfer technology (twisted pair) to LVDS (E-bus) and generates the necessary system voltage for the LVDS modules.
Type B-Nimis MC-I/O XR multifunction I/O modules combine digital and analog inputs and outputs in a single module. The digital input also has a counter function and is suitable for encoders.
Digital I/O
The digital signal mix consists of 8 inputs and 8 outputs. The outputs can also be used as digital inputs. Each input can count up to a frequency of 10 kHz. It can process 24 V encoder signals as well as count forward and backward.
Analog I/O
Depending on the module configuration, four additional connections may serve as inputs or outputs. Analog I/O functions include +/- 10 V and +/- 20 mA with a high resolution of up to 22 bits.
This is the module (MC-I/O XR02 ENC/C DIO 8/8) used in this project.
Use this IO Connector to connect the controller with EBUS.
Wiring
This is the MC-I/O XR02 ENC/C DIO 8/8 wiring.
Codesys Side
The next step is to set up the Codesys project.
Install ESI File
Get the ESI File of MC-I/O XR from BERGHOF and click Tools>Device Repository.
Select ESI File for MC-I/O XR.
Done!ESI File is installed.
Add EtherCAT Master
To add an EtherCAT Master, go to Device>Right click>Add Device.
Select Fieldbus>EtherCAT>Master>EtherCAT Master and add an EtherCAT Master.
Select Interface
Open EtherCAT Master and configure the Interface to be used as EtherCAT Master in General>Select.
Since EBUS is Ether1, Please set Eth1.
Scan for Devices
Download the EtherCAT Stack to the CPU once before using Auto Scan.
Next, click on EtherCAT Master>right click>Scan for Devices.
Done!MC-I/O XR02 has been found, use Copy to project to duplicate the Configuration to the project.
Result
Done!EtherCAT Configuration is now complete.
Configure EtherCAT Task
The next step is to build the EtherCAT Task.
Set Interval to 500us.
Program
Now we can create a Codesys program.
DUT_8BIT
This is a structure of 8BIT variables.
| TYPE DUT_8BIT : STRUCT b00 ,b01 ,b02 ,b03 ,b04 ,b05 ,b06 ,b07 :BIT; END_STRUCT END_TYPE |
DUT_IO
This is a structure that summarizes MC-I/O XR data.
| TYPE DUT_IO : STRUCT DigitalIN:DUT_8BIT; DigitalOut:DUT_8BIT; PLD_Veersion:USINT; STATUS:USINT; END_STRUCT END_TYPE |
GVL
Here is the Global Variable List that defines variables for MC-I/O XR I/O.
| {attribute ‘qualified_only’} VAR_GLOBAL IO1:DUT_IO; END_VAR |
pLocalIO
Create an LD2 program.
Network1
Network 1 initializes the Temp variable.
Network2
Network 2 is a timer that turns ON every 0.2 seconds.
Network3
Network 3 detects the rising output of the timer.
Network4
Network 4 shifts the Temp variable with the SHL function to the right of the current value.
Network5
Network 5 transfers the Temp variable to Process Output.
Mapping
Now we can map the GVL variables to EtherCAT I/O.
Downlaod
Download the Codesys project to the CPU.
Result
Done!EtherCAT communication has been established.
The RUN/STOP LED on the CPU is lit green (RUN MODE) and the EtherCAT/IO/Power LED on the E-IO XR02 is also lit green.
You can check the operation from this video.
Implementation2
The next step is to build an EtherCAT network with the MC-Pi controller from BERGHOF and EtherCAT Coupler from Beckhoff and OMRON.
Download ESI File
Download the ESI File from each company’s website.
Beckhoff
Here is the download location of the ESI File for Beckhoff EK1xxx.
OMRON
This is the download location of the ESI File for OMRON NX-ECC20x.
https://industrial.omron.eu/en/products/NX-ECC203
BERGHOF Side
Build your EtherCAT network with Eth2 from BERGHOF.
Configure Network via Web server
To enable BERGHOF’s Eth2, set Mode to Static in Configuration>Network>ETH2 and set IP address and NetMask.
Codesys Side
Let’s create a Codesys project.
Add EtherCAT Master
To add an EtherCAT Master, go to Device>Right click>Add Device.
Add EtherCAT Master.
Done!
Select Interface
Open EtherCAT Master and configure the Interface to be used as EtherCAT Master in General>Select.
Select Eth2.
Auto reset
Check the box General>Options>Automatically restart slaves so that the EtherCAT Master can automatically reset the slaves.
Scan for Devices
Download the EtherCAT Stack to the CPU once before using Auto Scan.
Next, click on EtherCAT Master>right click>Scan for Devices.
Done!OMRON and Beckhoff EtherCAT Slave were searched.
Result
Slaves from Beckhoff and OMRON were replicated in the project.
Mapping
This time, Mapping is done by absolute address between program variables and modules. The figure below uses EL1088 as an example.
Set the address at the beginning of EtherCAT I/O Mapping>Channel.
Program
The next step is to create a program.
GVL
Declare the Global Variable List according to the absolute address set in Mapping earlier.
| {attribute ‘qualified_only’} VAR_GLOBAL EL1088_IN AT %IB300 :DUT_8BIT; EL2088_OUT AT %QB301: DUT_8BIT; EL2004_OUT AT %QB302:DUT_8BIT; NXID5422 AT %IW100:UINT; NXOD5256 AT %QW100:UINT; END_VAR |
FieldbuStatus
This is a program to get the status of EtherCAT Master.
| PROGRAM FieldbuStatus VAR EtherCAT1_xError:BOOL; EtherCAT1_xConfigfinished:BOOL; EtherCAT1_DEDStatus:DED.DEVICE_STATE; EtherCAT1_DEDBusInfo:DED.BUS_INFO; _Frames:ARRAY[0..5]OF UDINT; _Times:ARRAY[0..3]OF LTIME; END_VAR |
| EtherCAT1_xError:= EtherCAT_Master.xError; EtherCAT1_xConfigfinished:= EtherCAT_Master.xConfigFinished; EtherCAT1_DEDStatus:= EtherCAT_Master.GetDeviceState(); EtherCAT_Master.GetBusInfo( EtherCAT1_DEDBusInfo); EtherCAT_Master.GetStatistics ( udiFramesPerSecond=>_Frames[0] ,udiLostCyclesCount=>_Frames[1] ,udiLostFrameCount=>_Frames[2] ,udiRxErrorCount=>_Frames[3] ,udiSendFrameCount=>_Frames[4] ,udiTxErrorCount=>_Frames[5] ,ltRecvAvg=>_Times[0] ,ltRecvMax=>_Times[1] ,ltSendAvg=>_Times[2] ,ltSendMax=>_Times[3] ); |
pCATIO
This is a simple program that softens 16 channels of DO module installed in OMRON’s EtherCAT Coupler in order, and also softens the output of Beckhoff’s EL2004 every time OMRON’s DI module (Channel 3) is turned on. The program is as follows.
| PROGRAM pCATIO VAR temp:UINT; temp2:USINT; TON:TON; R_TRIG:R_TRIG; R_TRIG2:R_TRIG; END_VAR |
| IF temp=0 THEN temp.15:=TRUE; END_IF IF temp2 =0 THEN temp2.3:=TRUE; END_IF R_TRIG(CLK:=TON.Q); TON(IN:=NOT TON.Q,PT:=T#0.2S); IF TON.Q THEN temp:=SHR(temp,1); END_IF; MEM.MemMove(ADR(temp),ADR(GVL_CAT.NXOD5256),SIZEOF(temp)); GVL_CAT.EL2088_OUT:=GVL_CAT.EL1088_IN; R_TRIG2(CLK:=GVL_CAT.NXID5422.3); IF R_TRIG2.Q THEN IF temp2.3 THEN temp2.3:=FALSE; temp2.0:=TRUE; ELSE temp2:=SHL(temp2,1); END_IF END_IF MEM.MemMove(ADR(temp2),ADR(GVL_CAT.EL2004_OUT),SIZEOF(temp2)); |
Downlaod
Download the Codesys project to the CPU.
Result
Done!Communication was established between the BERGHOF CPU and the OMRON/Beckhoff EtherCAT Coupler.
You can see the operation of softening the OD5256 output of the OMRON ECC-203 from BERGHOF’s MC-PI controller in this video.
You can see the linkage operation of OMRON ECC-203 and Beckhoff’s EK1101 from BERGHOF’s MC-PI controller in this video.