This series explains various FC and FB functions in Sysmac Studio with programming examples. This time, we introduce the following FB functions: FileOpen, FileSeek, FileWrite, FileWriteVar, FileRead, FileReadVar, and FileClose.
Let’s enjoy FA.

Foreword
Thank you from the bottom of my heart for visiting my technical blog and YouTube channel.
We are currently running the “Takahashi Chris” radio show with Full-san (full@桜 八重 (@fulhause) / X) which I deliver every Wednesday night.
https://open.spotify.com/show/6lsWTSSeaOJCGriCS9O8O4
Sharing, not hoarding, technical knowledge
We publish technical information related to factory production technology and control systems for free, through blogs and videos.
With the belief that “knowledge should be accessible to everyone,” we share practical know-how and real-world troubleshooting cases from our own field experience.
The reason we keep it all free is simple: to help reduce the number of people who struggle because they simply didn’t know.
If you’ve ever thought:
- “Will this PLC and device combination actually work?”
- “I’m having trouble with EtherCAT communication—can someone test it?”
- “I want to try this remote I/O, but we don’t have the testing environment in-house…”
Feel free to reach out!If lending equipment or sharing your configuration is possible, we’re happy to verify it and share the results through articles and videos.
(We can keep company/product names anonymous if requested.)
How can you support us?
Currently, our activities are nearly all unpaid, but creating articles and videos takes time and a proper testing environment.If you’d like to support us in continuing and expanding this content, your kind help would mean a lot.
Membership (Support our radio show)
This support plan is designed to enhance radio with Mr Full.
https://note.com/fulhause/membership/join
Amazon Gift List (equipment & books for content production)
Lists equipment and books required for content creation.
https://www.amazon.co.jp/hz/wishlist/ls/H7W3RRD7C5QG?ref_=wl_share
Patreon (Support articles & video creation)
Your small monthly support will help to improve the environment for writing and verifying articles.
https://www.patreon.com/user?u=84249391
Paypal
A little help goes a long way.
https://paypal.me/soup01threes?country.x=JP&locale.x=ja_JP
Just trying to share things that could’ve helped someone—if only they’d known.
Your support helps make knowledge sharing more open and sustainable.
Thank you for being with us.
soup01threes*gmail.com
Technical knowledge shouldn’t be kept to ourselves.
Explanation
Important Notes!
- Execution of this instruction continues until completion, even if the Execute value changes to FALSE or the execution time exceeds the task period. When execution is complete, the Done value changes to TRUE. Use this to confirm successful completion of the process.
- To obtain the FileID value, you must use the FileOpen instruction beforehand.
- Files opened with the FileOpen instruction must be closed using this instruction after use.
- If the CPU unit’s operating mode changes to PROGRAM mode, or if a controller error of major fault level occurs, open files are closed by the system. Read or write operations in progress will continue to completion.
- For NJ/NX Series CPU Units, if the SD memory card power switch is pressed to stop power while a file is open, the file will not be corrupted. However, the file remains open. Use the FileClose instruction to close the file.
- For NJ/NX Series CPU Units, if the SD memory card is removed before pressing the SD memory card power switch while a file is open, the file contents may become corrupted. Always turn off the power before removing the SD memory card.
- For NJ/NX Series CPU Units, if the SD memory card is removed before pressing the SD memory card power switch while a file is open, the file remains open. Use the FileClose instruction to close the file.
- For NJ/NX Series CPU Units, if a file is open when power is stopped or the SD memory card is removed, the file remains open. However, even if the SD memory card is reinserted, the file cannot be read from or written to. To read from or write to the file, close the file and then reopen it.
- Do not access the same file simultaneously. Implement exclusive control for SD memory card instructions within the user program.
-
An error occurs in the following cases. Error changes to TRUE.
- The SD memory card is not in a usable state.
- The file specified by FileID does not exist.
- The file specified by FileID is already closed.
- The file specified by FileID is being accessed.
- An error occurs during access to the SD memory card, resulting in access failure.
FB
The following section describes the function blocks used in this article’s sample program.
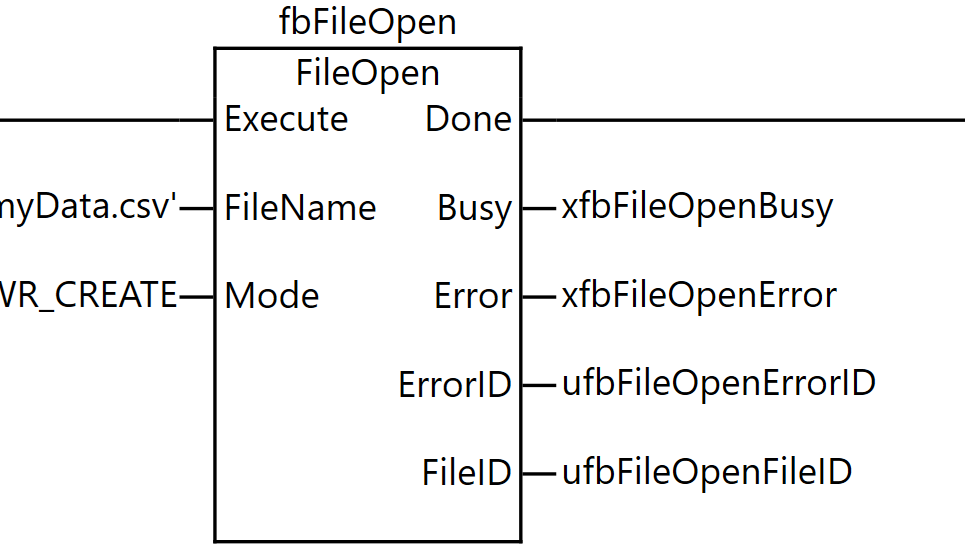
FileOpen
The FileOpen instruction opens the file specified by FileName on the SD memory card in the mode specified by Mode.
The result is output to the file ID FileID. The FileID is used to specify the file in other instructions such as FileRead and FileWrite.
The data type of Mode is the enumeration type _eFOPEN_MODE. The meanings of the enumerators are as follows:
Enumerator | Meaning |
|---|---|
READ_EXIST | Use this value to open an existing text file for reading. The file is read from the beginning. |
RDWR_EXIST | Use this value to open an existing file for reading and writing. The file is read and written from the beginning. |
WRITE_CREATE | Use this value to open a file for writing. If the file already exists, the contents are discarded and the file size is set to 0. If the file does not exist, a new file is created. The file is written from the beginning. However, if the file already exists and is write-protected, an error occurs and the file is not opened. |
RDWR_CREATE | Use this value to open a file for reading and writing. If the file already exists, the contents are discarded and the file size is set to 0. If the file does not exist, a new file is created. The file is read and written from the beginning. |
WRITE_APPEND | Use this value to open a file and append data. If the file does not exist, a new file is created. Data is appended to the end of the file. However, if the file already exists and is write-protected, an error occurs and the file is not opened. |
RDWR_APPEND | Use this value to open a file for reading and appending data. If the file does not exist, a new file is created. The file is read from the beginning. Data is appended to the end of the file. |
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description | Valid Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
FileName | File name | Input | Name of the file to open | Maximum 66 bytes (65 alphanumeric characters + trailing NULL character) |
Mode | Open mode | Input | Mode for opening the file | |
FileID | File ID | Output | ID of the opened file | Depends on data type |
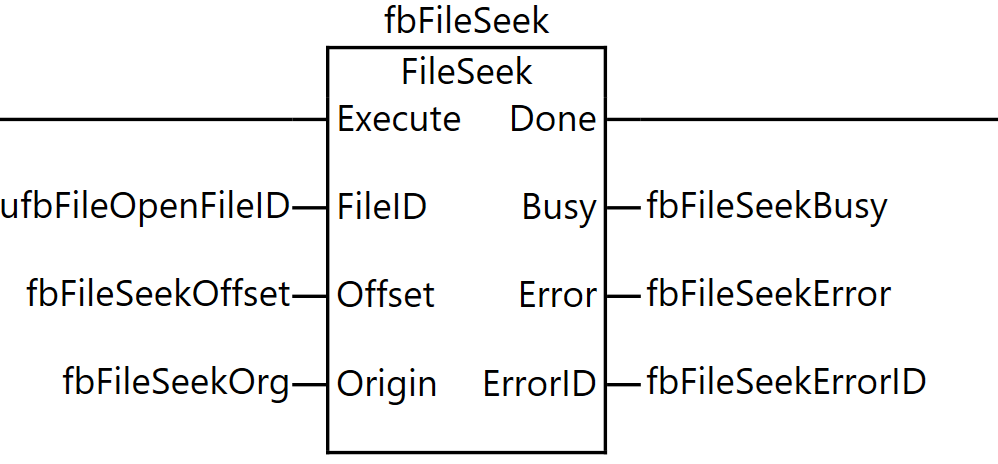
FileSeek
The FileSeek instruction sets the file position indicator for the specified file on the SD memory card. The file position indicator refers to the position within the file where reading or writing begins when instructions such as FileRead or FileWrite are executed.
For example, to read from the beginning of a file, use the FileSeek instruction to set the file position indicator to the beginning of the file, then execute the FileRead instruction. The file position indicator is set to a position offset from the reference position Origin.
The data type of Origin is the enumeration type _eFSEEK_ORIGIN. The meanings of the enumerators are as follows:
Enumerator | Meaning |
|---|---|
_SEEK_SET | Beginning of the file |
_SEEK_CUR | Current file position indicator location |
_SEEK_END | End of the file |
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
FileID | File ID | Input | ID of the file for which to set the file position indicator |
Offset | Offset | Input | Offset from Origin |
Origin | Reference position | Input | Reference position for the file position indicator |
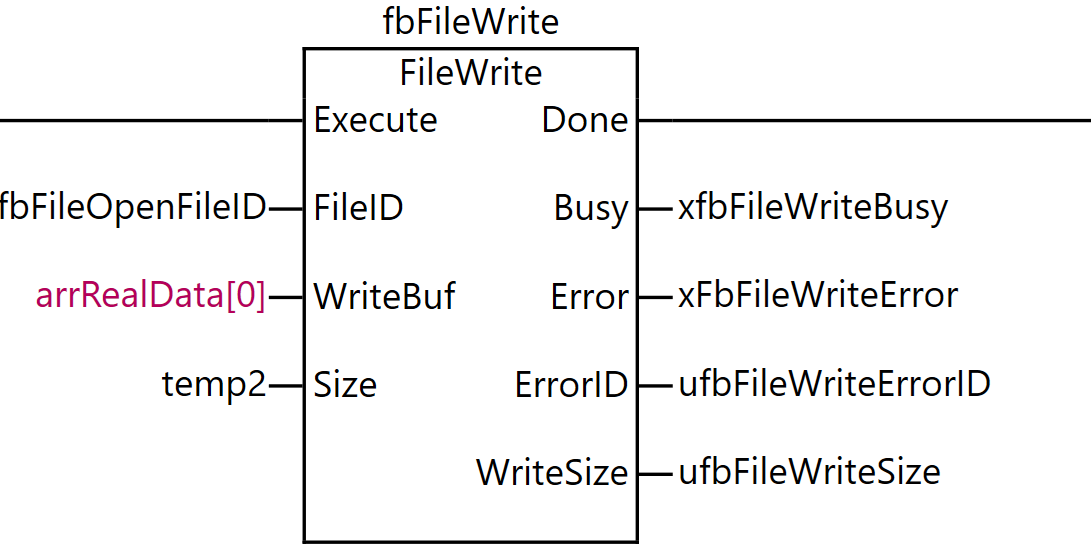
FileWrite
The FileWrite instruction writes data to the specified file on the SD memory card. This instruction writes data to the position indicated by the file position indicator of the file specified by the file ID FileID.
The file position indicator must be set to the desired location in advance using the FileSeek instruction. When writing, the contents of the write buffer WriteBuf[] are written to the file.
The amount of data written is the size of the data type of WriteBuf[] multiplied by Size, that is, Size elements of WriteBuf[]. Note that WriteBuf[] can also be specified as an array of enumeration types or structures.
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
FileID | File ID | Input | ID of the file to write to |
WriteBuf[] (array) | Write buffer | Input | Data to write |
Size | Number of elements to write | Input | Number of elements to write |
WriteSize | Number of elements written | Output | Actual number of elements written |
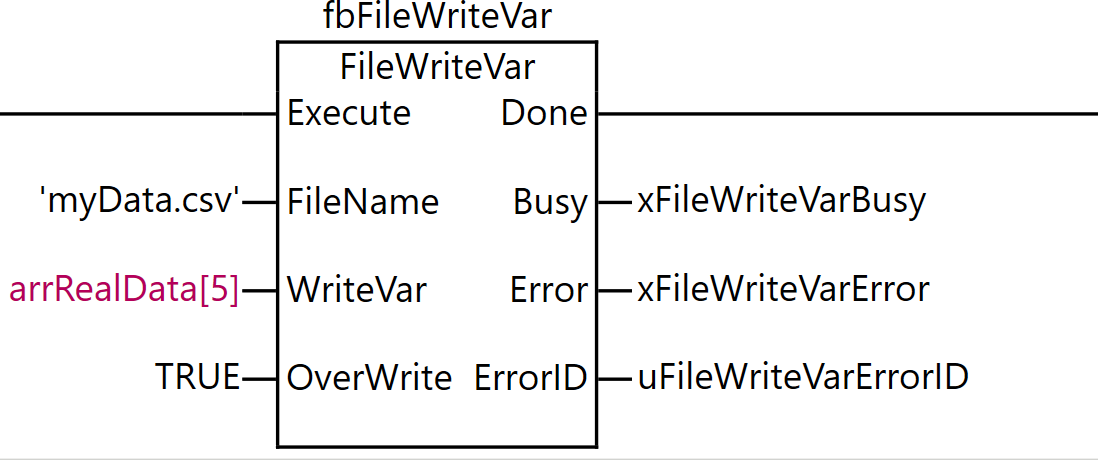
FileWriteVar
The FileWriteVar instruction writes the value of the variable WriteVar to the file specified by FileName on the SD memory card in binary format. WriteVar can be specified as an enumeration type, array, array element, structure, or structure member.
If a file named FileName does not exist on the SD memory card, it will be newly created. FileName can include a path, and if the specified directory does not exist on the SD memory card, it will be created automatically. However, the directory is only created if only the lowest directory level of the specified path does not exist.
On the other hand, if a file named FileName already exists on the SD memory card, processing is executed according to the value of overwrite permission OverWrite.
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description | Valid Range |
|---|---|---|---|---|
FileName | File name | Input | Name of the file to write the variable to | Maximum 66 bytes (65 alphanumeric characters + trailing NULL character) |
WriteVar | Variable | Input | Variable to write | – |
OverWrite | Overwrite permission | Input | TRUE: Allow overwrite.<br>FALSE: Prohibit overwrite. | Depends on data type |
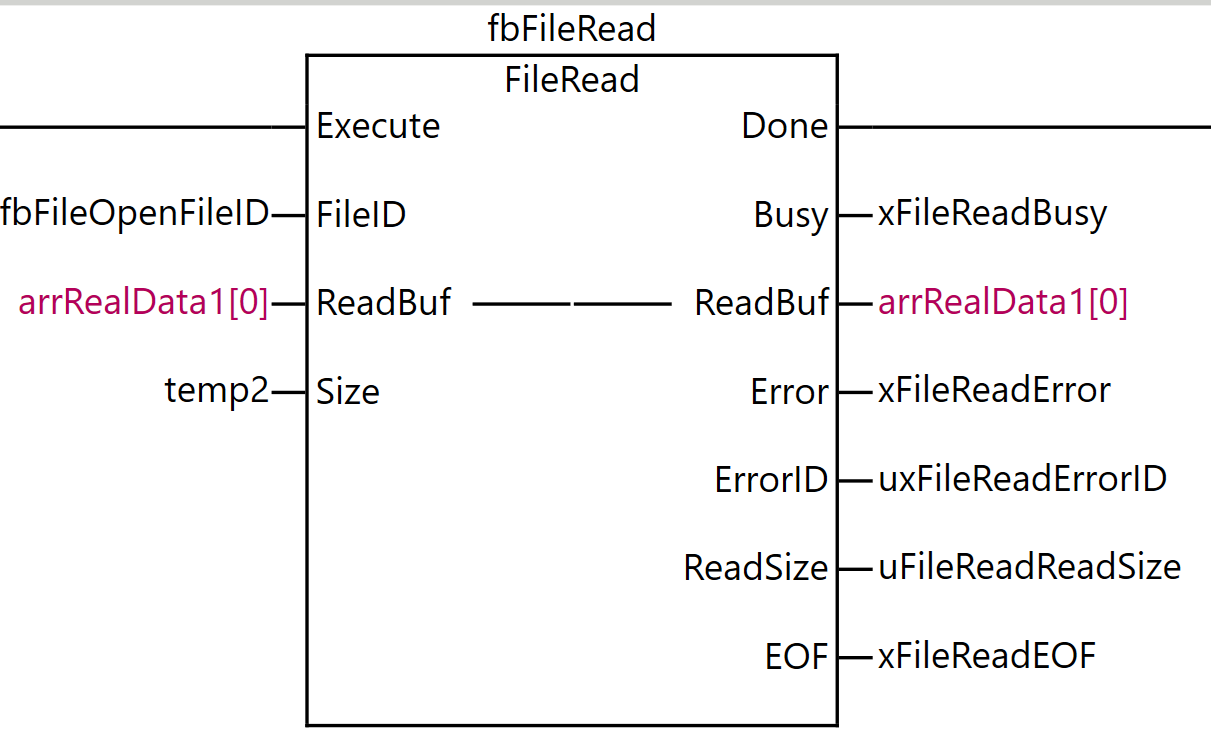
FileRead
The FileRead instruction reads data from the specified file on the SD memory card. This instruction reads data from the position indicated by the file position indicator of the file specified by the file ID FileID, and stores it in the read buffer ReadBuf[].
The file position indicator must be set to the desired location in advance using the FileSeek instruction. The amount of data to read is the size of the data type of ReadBuf[] multiplied by Size, that is, Size elements of ReadBuf[]. Note that ReadBuf[] can also be specified as an array of enumeration types or structures.
The actual number of elements read is stored in ReadSize. Normally, Size and ReadSize have the same value, but even if the amount of data from the file position indicator to the end of the file is smaller than Size, no error occurs and the data up to the end of the file is stored in ReadBuf[]. In this case, the value of ReadSize will be smaller than the value of Size.
When data has been read up to the end of the file, the end of file EOF changes to TRUE. Otherwise, the value of EOF is FALSE.
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
FileID | File ID | Input | ID of the file to read from |
Size | Number of elements to read | Input | Number of elements to read |
ReadBuf[] (array) | Read buffer | In-out | Buffer to store the read data |
ReadSize | Number of elements read | Output | Actual number of elements read |
EOF | End of file | Output | Whether the end of file has been reached TRUE: Reached. FALSE: Not reached. |
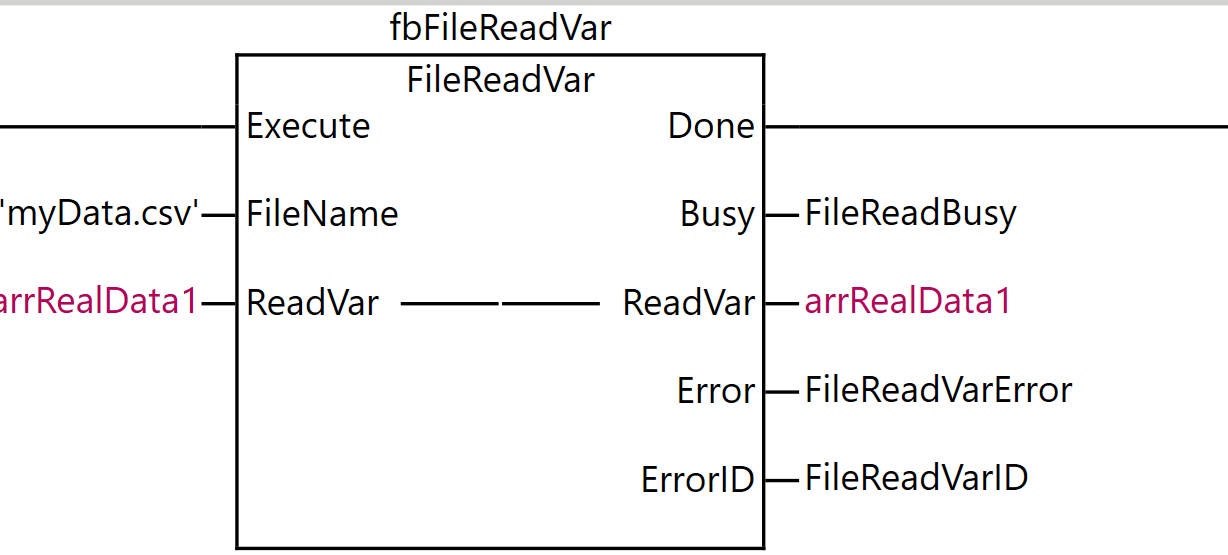
FileReadVar
The FileReadVar instruction reads the contents of the specified file on the SD memory card as binary data and writes it to a variable. This instruction reads the contents of the file specified by FileName from the SD memory card as binary data. The read contents are assigned to the destination variable ReadVar.
ReadVar can be specified as an enumeration type, array, array element, structure, or structure member.
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
FileName | File name | Input | Name of the file to read from |
ReadVar | Destination variable | In-out | Variable to write the read value to |
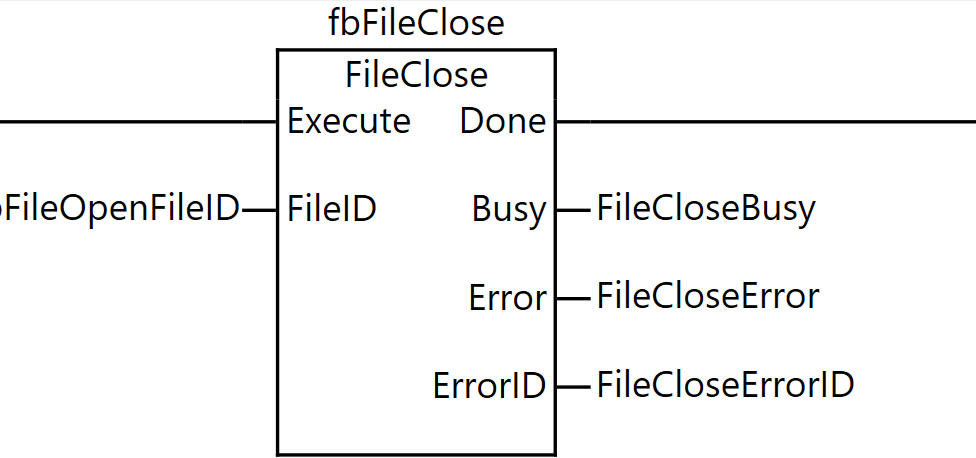
FileClose
The FileClose instruction closes the specified file on the SD memory card. This instruction closes the file specified by FileID on the SD memory card.
Item | Meaning | I/O | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
FileID | File ID | Input | ID of the file to close |
Related system definition variables
Name | Meaning | Data Type | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
_Card1Ready | SD memory card ready flag | BOOL | This flag indicates whether the SD memory card can be accessed by instructions and communication commands. TRUE: Available. FALSE: Not available. |
_Card1Protect | SD memory card write protect flag | BOOL | This flag indicates whether the SD memory card is write-protected when it is inserted and ready for use. TRUE: Write-protected. FALSE: Not write-protected. |
_Card1Err | SD memory card error flag | BOOL | This flag indicates whether an unusable SD memory card is mounted or a format error has occurred.TRUE: Error.FALSE: No error. |
_Card1Access | SD memory card access flag | BOOL | This flag indicates whether the SD memory card is currently being accessed. TRUE: Being accessed. FALSE: Not being accessed. |
_Card1PowerFail | SD memory card power failure flag | BOOL | This flag indicates whether power was interrupted during access and an error occurred at the completion of processing. This flag is not cleared automatically. TRUE: Error. FALSE: No error. |
Implementation
Now let’s actually implement a program to read and write files.
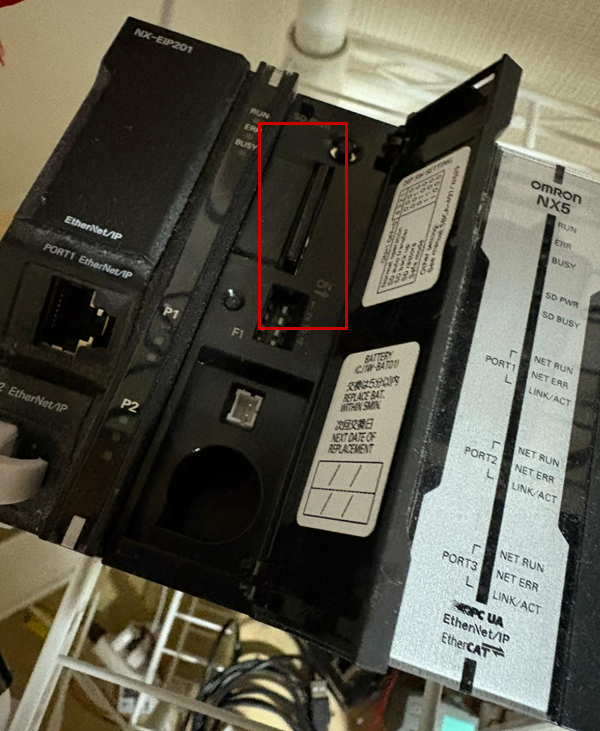
Insert the SD card
Please insert the SD card into the following slot on the Omron NX CPU.

プログラム
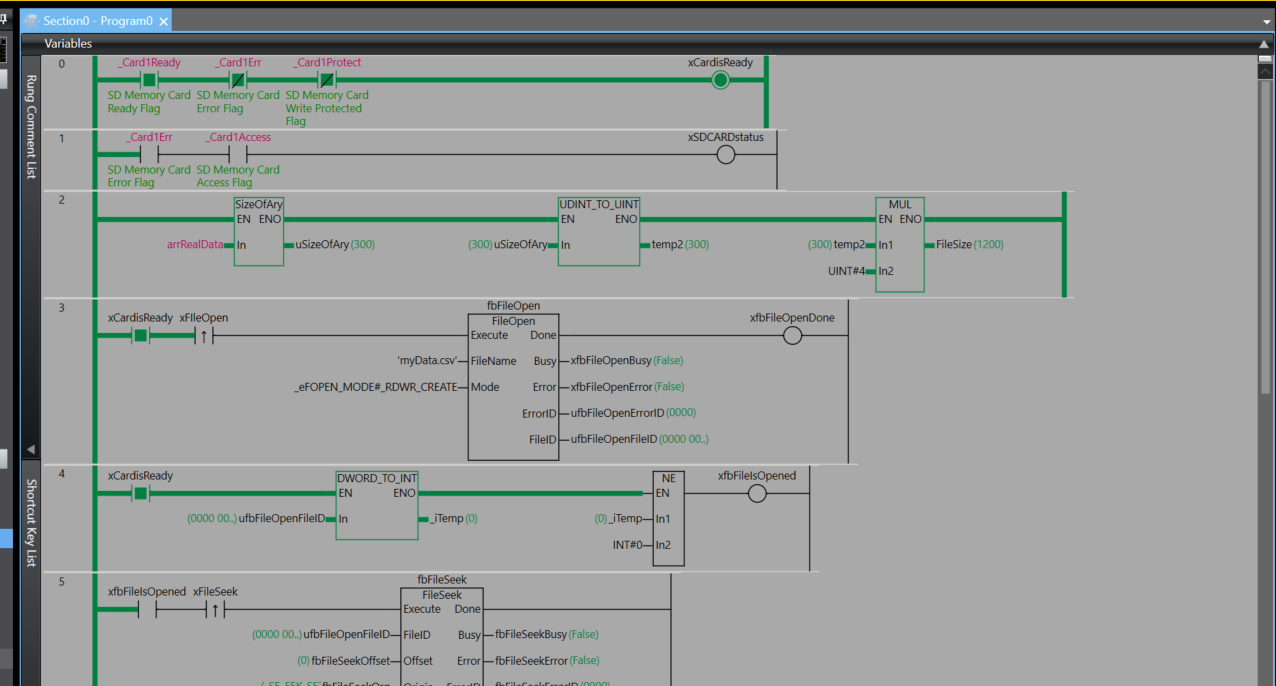
This is the program for this article, and we’ll now explain what Rung is.
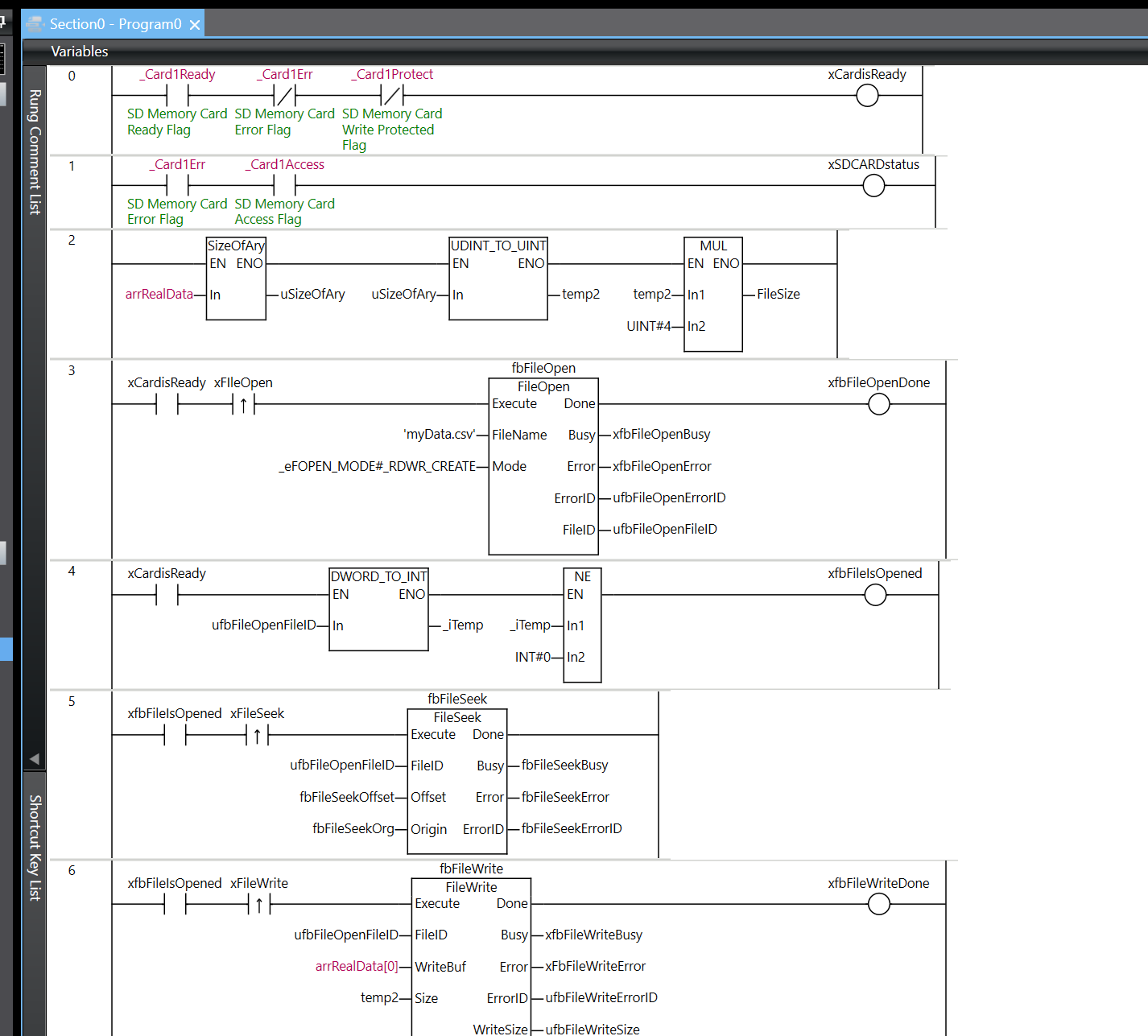
Rung0
Rung 0 is a logic circuit for determining whether the SD memory card is in a usable state.
In the program, three conditions are connected in series and evaluated. First, it checks that _Card1Ready (SD memory card ready flag) is ON, then that _Card1Err (SD memory card error flag) is OFF, and finally that _Card1Protect (SD memory card write protect flag) is OFF.
Only when all three conditions are met—that is, when the SD memory card is in the ready state, no error has occurred, and write protection is not enabled—does the output variable xCardisReady become TRUE.
Rung1
Rung 1 is a logic circuit for monitoring whether the SD memory card is operating normally.
In the program, two conditions are connected in series and evaluated. It checks that _Card1Err (SD memory card error flag) is OFF, and that _Card1Access (SD memory card access flag) is OFF.
Only when both conditions are met—that is, when no error has occurred on the SD memory card and it is not currently being accessed—does the output variable xSDCARDstatus become TRUE.

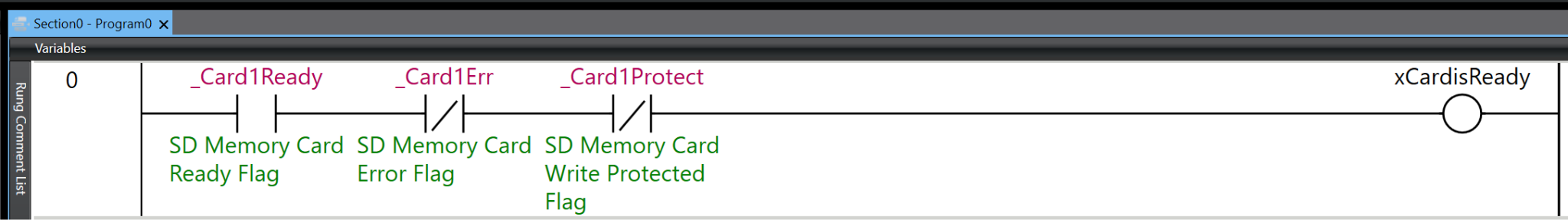
Rung2
Rung 2 is a process for calculating the file size in bytes from the size of the array.
The program is executed by connecting three function blocks in series. First, the SizeOfAry instruction obtains the number of elements in the array arrRealData and stores the result in uSizeOfAry. Next, the UDINT_TO_UINT instruction converts the data type of uSizeOfAry and outputs it to temp2. Finally, the MUL instruction multiplies temp2 by UINT#4 (4 bytes) and stores the final file size in FileSize.
Through this series of processes, the data size of the entire array is calculated in bytes by multiplying the number of array elements by the size of each element (4 bytes). This is used to calculate in advance the data size required when writing to or reading from a file.
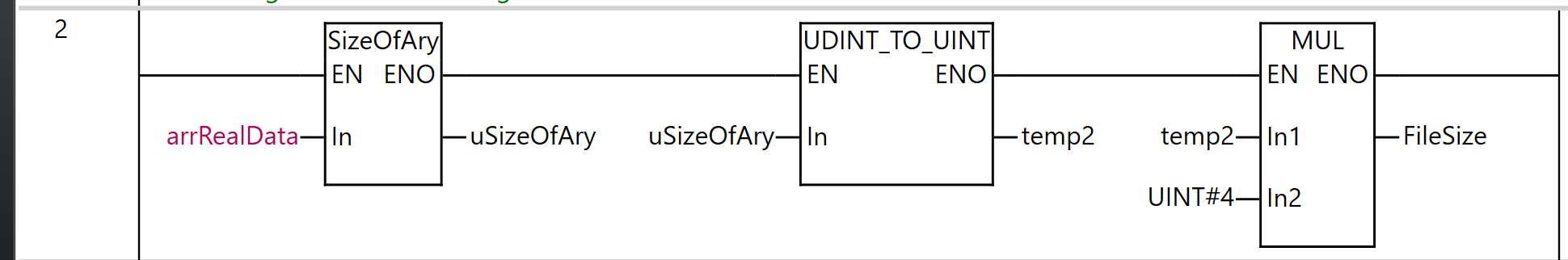
Rung3
Rung 3 is a process for opening a file on the SD memory card.
As the execution condition for the program, when xCardisReady (SD memory card is available) is ON and the rising edge of xFIleOpen (file open command) is detected, fbFileOpen (FileOpen instruction) is executed.
For the FileOpen instruction, ‘myData.csv’ is specified as FileName (file name), and _eFOPEN_MODE#_RDWR_CREATE (open for reading and writing, discard contents and create new if existing) is set as Mode (open mode).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Done output is stored in xfbFileOpenDone, the Busy output in xfbFileOpenBusy, the Error output in xfbFileOpenError, the ErrorID output in ufbFileOpenErrorID, and the FileID output in ufbFileOpenFileID.
Through this process, the specified CSV file is opened in a readable and writable state, and a file ID for use in subsequent processing can be obtained.
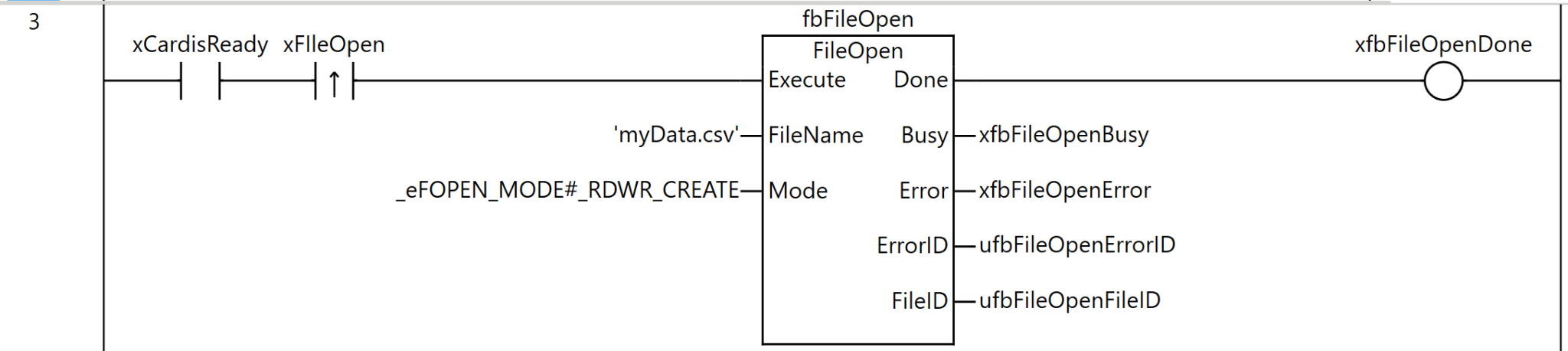
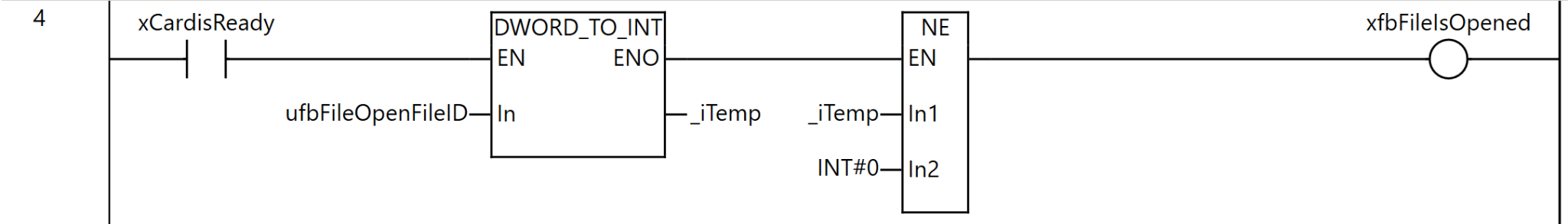
Rung4
Rung 4 is a process for checking whether the file has been opened successfully.
As the execution condition for the program, it is executed when xCardisReady (SD memory card is available) is ON. First, the DWORD_TO_INT instruction converts ufbFileOpenFileID (the file ID obtained by the FileOpen instruction) to INT type and stores it in _iTemp. Next, the NE instruction compares _iTemp with INT#0 (zero).
If _iTemp is not zero—that is, if the file ID is a valid value—xfbFileIsOpened (a flag indicating that the file is open) becomes TRUE.
Through this process, it can be confirmed that the FileOpen instruction succeeded and a valid file ID was obtained, and it can be determined that the system is in a state where subsequent file operations (reading and writing) can be executed safely.
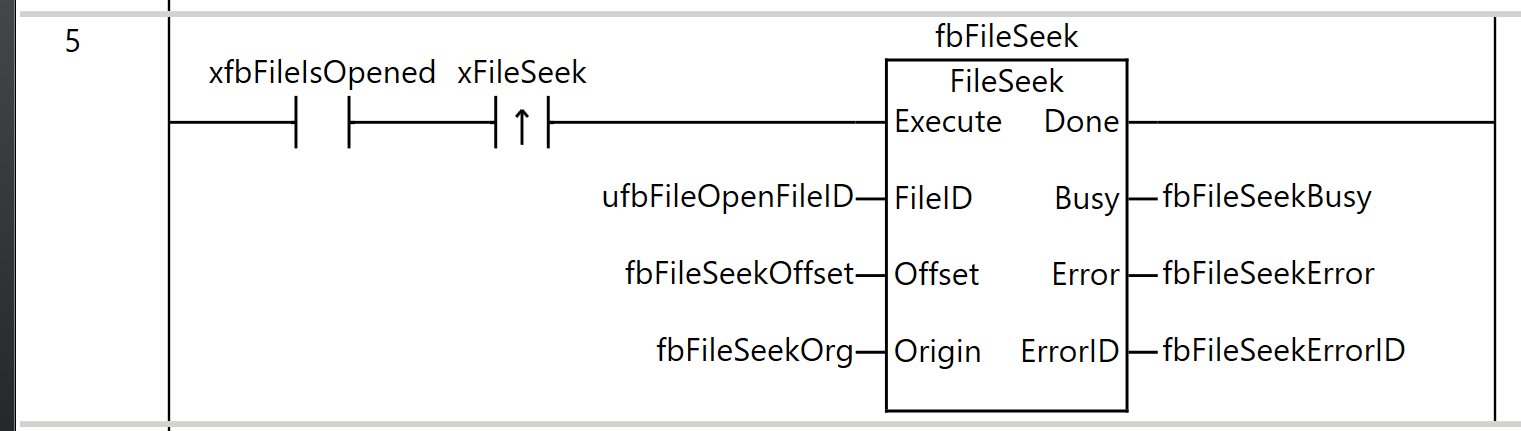
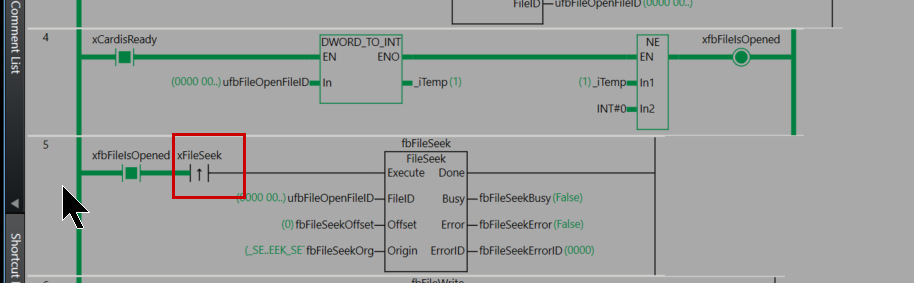
Rung5
Rung 5 is a process for setting the file position indicator within the opened file.
As the execution condition for the program, when xfbFileIsOpened (file is open) is ON and the rising edge of xFileSeek (file seek command) is detected, fbFileSeek (FileSeek instruction) is executed.
For the FileSeek instruction, ufbFileOpenFileID (the file ID obtained by the FileOpen instruction) is specified as FileID (file ID), fbFileSeekOffset is set as Offset (offset), and fbFileSeekOrg is set as Origin (reference position).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Busy output is stored in fbFileSeekBusy, the Error output in fbFileSeekError, and the ErrorID output in fbFileSeekErrorID.
Through this process, the file position indicator is moved based on the specified offset and reference position, allowing data to be read from or written to any position in the file using subsequent FileRead or FileWrite instructions.
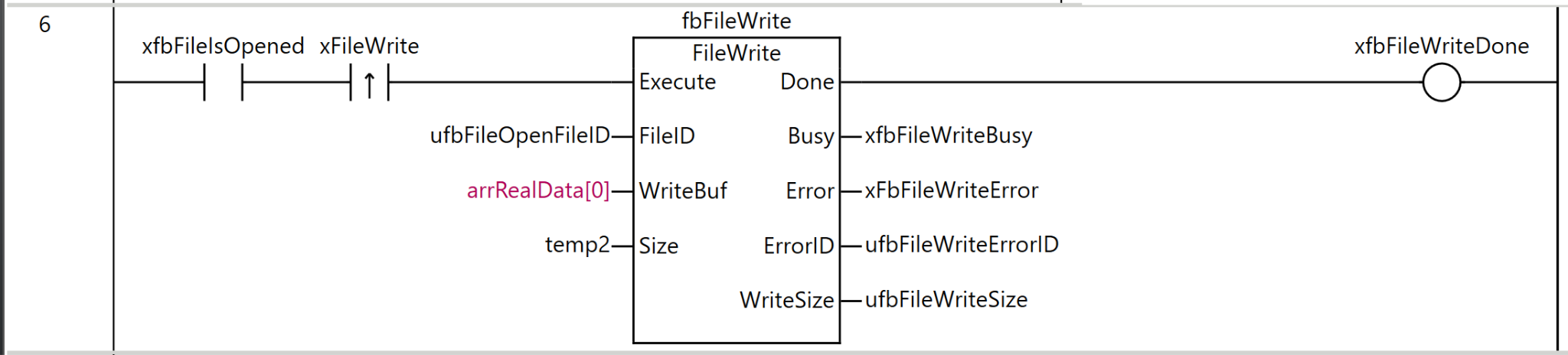
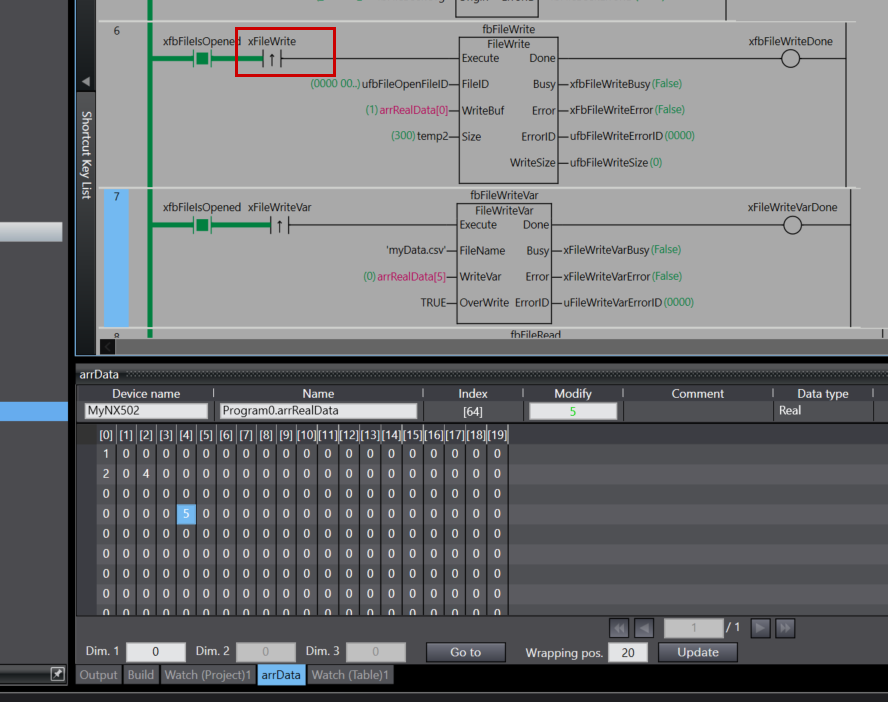
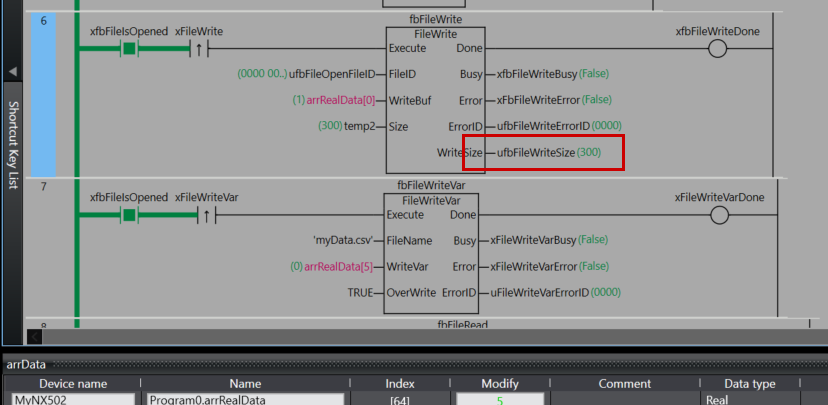
Rung6
Rung 6 is a process for writing data to the opened file.
As the execution condition for the program, when xfbFileIsOpened (file is open) is ON and the rising edge of xFileWrite (file write command) is detected, fbFileWrite (FileWrite instruction) is executed.
For the FileWrite instruction, ufbFileOpenFileID (the file ID obtained by the FileOpen instruction) is specified as FileID (file ID), arrRealData[0] is set as WriteBuf (write buffer), and temp2 is set as Size (number of elements to write).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Done output is stored in xfbFileWriteDone, the Busy output in xfbFileWriteBusy, the Error output in xfbFileWriteError, the ErrorID output in ufbFileWriteErrorID, and WriteSize (actual number of elements written) in ufbFileWriteSize.
Through this process, the contents of the array arrRealData can be written to the file at the file position indicator location. The amount of data written will be the number of elements specified by temp2.
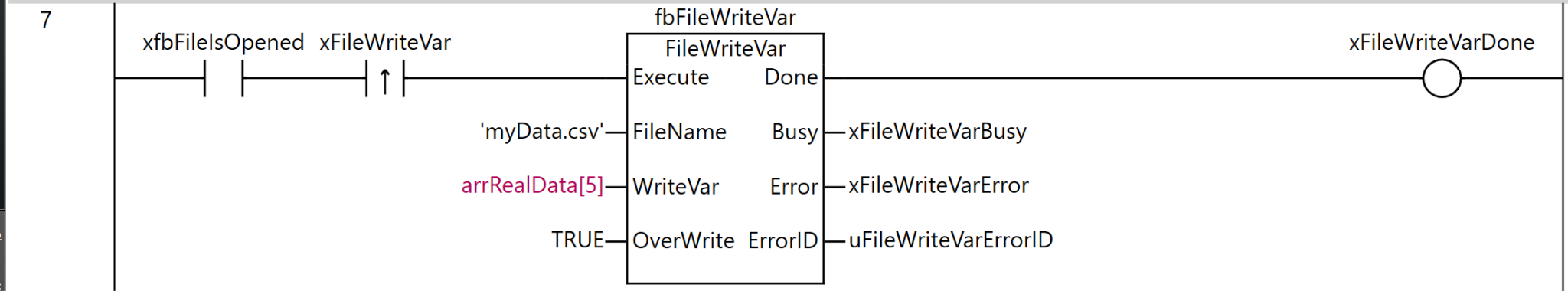
Rung7
Rung 7 is a process for writing the value of a variable directly to a file.
As the execution condition for the program, when xfbFileIsOpened (file is open) is ON and the rising edge of xFileWriteVar (file variable write command) is detected, fbFileWriteVar (FileWriteVar instruction) is executed.
For the FileWriteVar instruction, ‘myData.csv’ is specified as FileName (file name), arrRealData[5] is set as WriteVar (variable to write), and TRUE (allow overwrite) is set as OverWrite (overwrite permission).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Done output is stored in xFileWriteVarDone, the Busy output in xFileWriteVarBusy, the Error output in xFileWriteVarError, and the ErrorID output in uFileWriteVarErrorID.
Through this process, the value of a specific element of the array arrRealData can be written directly to the specified file in binary format. If the file already exists, it will be overwritten.
The FileWriteVar instruction is a convenient method that allows saving variable values to a file independently, without using FileOpen or FileSeek.
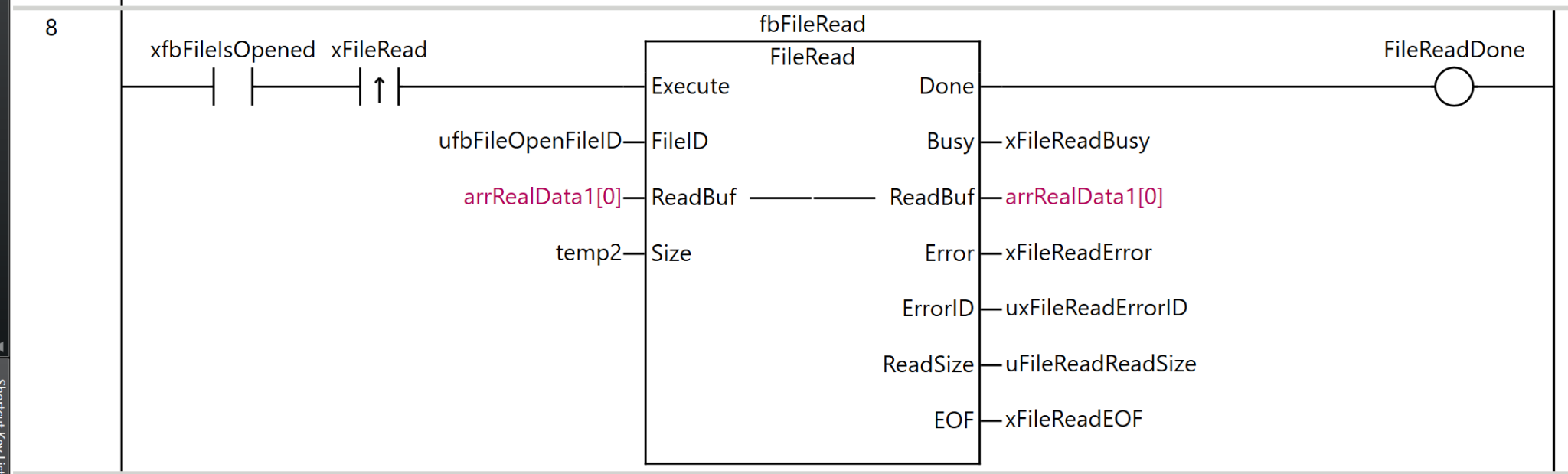
Rung8
Rung 8 is a process for reading data from the opened file.
As the execution condition for the program, when xfbFileIsOpened (file is open) is ON and the rising edge of xFileRead (file read command) is detected, fbFileRead (FileRead instruction) is executed.
For the FileRead instruction, ufbFileOpenFileID (the file ID obtained by the FileOpen instruction) is specified as FileID (file ID), arrRealData[0] is set as ReadBuf (read buffer), and temp2 is set as Size (number of elements to read).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Done output is stored in FileReadDone, the Busy output in xFileReadBusy, the ReadBuf output in arrRealData1[0], the Error output in xFileReadError, the ErrorID output in uxFileReadErrorID, ReadSize (actual number of elements read) in uFileReadReadSize, and EOF (end of file flag) in xFileReadEOF.
Through this process, data for the number of elements specified by temp2 can be read from the file position indicator location and stored in the array arrRealData1. If the end of the file has been reached, the EOF flag becomes TRUE.
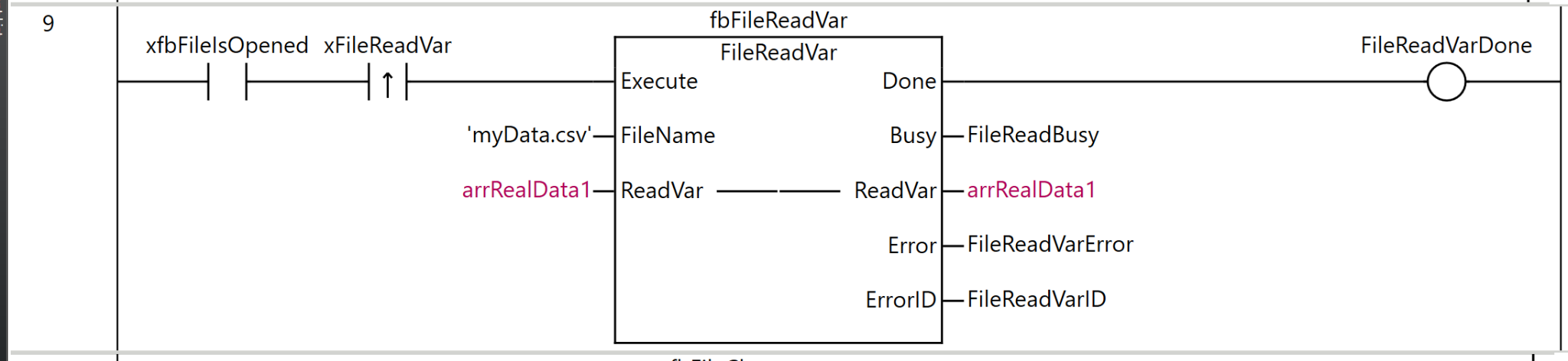
Rung9
Rung 9 is a process for reading data directly from a file into a variable.
As the execution condition for the program, when xfbFileIsOpened (file is open) is ON and the rising edge of xFileReadVar (file variable read command) is detected, fbFileReadVar (FileReadVar instruction) is executed.
For the FileReadVar instruction, ‘myData.csv’ is specified as FileName (file name), and arrRealData1 is set as ReadVar (destination variable).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Done output is stored in FileReadVarDone, the Busy output in FileReadBusy, the ReadVar output in arrRealData1, the Error output in FileReadVarError, and the ErrorID output in FileReadVarID.
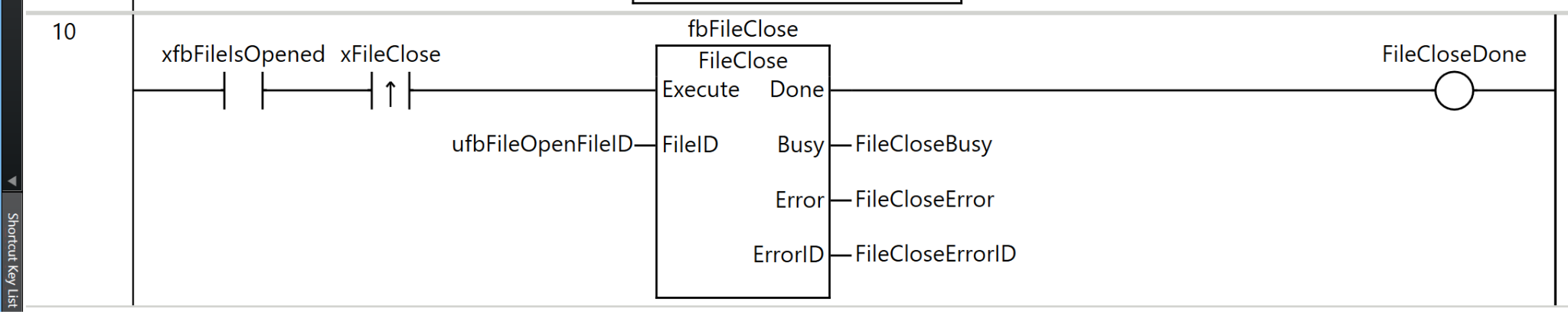
Rung10
Rung 10 is a process for closing the opened file.
As the execution condition for the program, when xfbFileIsOpened (file is open) is ON and the rising edge of xFileClose (file close command) is detected, fbFileClose (FileClose instruction) is executed.
For the FileClose instruction, ufbFileOpenFileID (the file ID obtained by the FileOpen instruction) is specified as FileID (file ID).
As the execution results of the instruction, the Done output is stored in FileCloseDone, the Busy output in FileCloseBusy, the Error output in FileCloseError, and the ErrorID output in FileCloseErrorID.
Through this process, the file opened by the FileOpen instruction can be properly closed. It is important to always close the file using the FileClose instruction after use is complete. This ensures data integrity and guarantees that writing to the SD memory card is completed successfully.
Download
Finally, let’s download the program to the NX CPU.
結果
xCardisReady being True indicates that the NX CPU currently recognizes the SD card.
The file opened successfully.
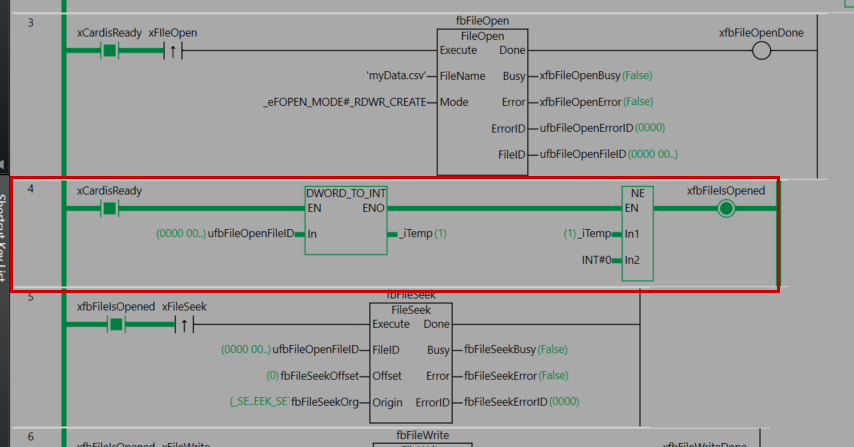
Set xFileSeek to True to set the start position for reading and writing to the file.
Next, set xFileWrite to True and write the data to the SD card.
uifbFileWriteSize is 300, meaning 300 data items were written to the SD card.
Next, set xFileRead to True and try reading data from the SD card.
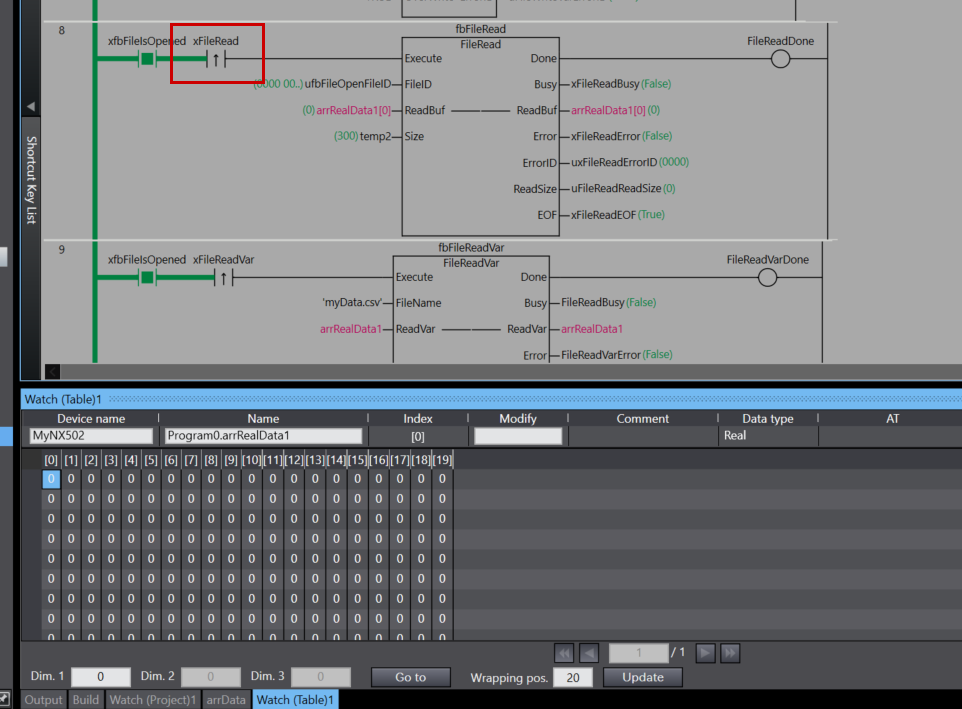
Done!
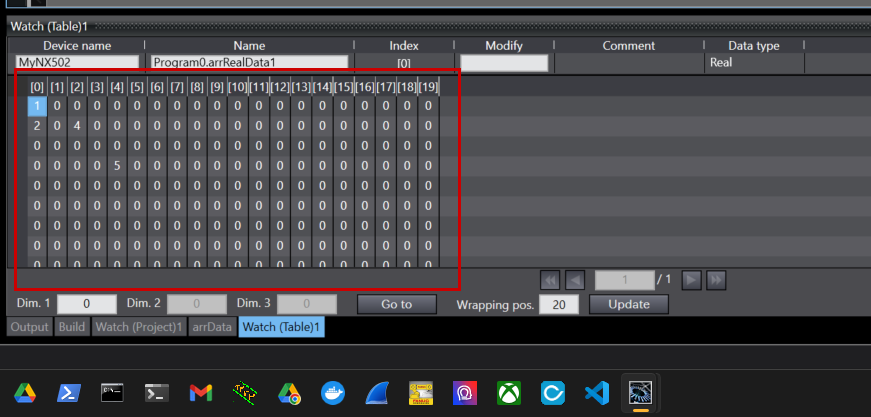
Finally, I confirmed that the contents of the SD card contained the binary file of the data I saved earlier.