Here is a new article series using Phoenix Contact’s Security Router FL MGUARD 1105!Cyber security is one of the essential issues in our FA industry today, and I had to study it myself.
In this second episode, I will explain Port forwarding and how to configure it.
Come on, let’s enjoy FA.
Reference Link
http://soup01.com/en/category/phoenixcontact/fl-mguard-en/
Reference Video
Phoenix Contact.Open box with FL MGUARD 1105!!
Cybersecurity…
In the previous article we briefly listed security measures related to devices and solutions, now let’s talk about security related to PC-paced software. PC-based software is used to set up, configure devices, networks, solutions,program, and monitor devices, networks, and solutions.Engineering software can also manipulate devices and solutions.To reduce the risk of their tampering, perform regular security assessments.
Recommendation
✓PC Hardening and Organizational Measures
Ensure that all PCs used in the automation solution environment are protected from security-related operations.
- Boot PCs regularly and only from data carriers protected from tampering
- Set limited access rights only for personnel who absolutely need authorization
- Protect systems from unauthorized access with strong passwords and rules to maintain their strength
- Stop unused services
- Uninstall unused software
- Use firewalls to restrict access
- Use permission list tools to protect critical directories and data from unauthorized changes
- Enable security-related event logging according to security directives and legal requirements for data protection
- Enable update functionality in accordance with security directives
- Enable automatic screen lock feature and automatic logout after a specified time
- Perform regular backups
- Use only data and software from approved sources
- Do not use hyperlinks from unknown sources, such as email
✓Use the latest software
Always use the latest software version (e.g., team engineering software, operating system, etc.).
- Check each product page for software updates
- Refer to the change notes for each software version
- Check each product page for security advisories regarding published security vulnerabilities Phoenix Contact products are on this page.
https://www.phoenixcontact.com/de-de/service-und-support/psirt?cpn=murl_psirt&murl=psirt
Routes?
When the device is operating in router mode, it acts as a gateway between different subnets.
Using static settings for Routes allows the device to reach network destinations that are unknown to the default gateway.These destinations can also be accessed by connected network clients that use the device as their default gateway.
The Router can route data between the device’s two network interfaces (netzones), but by factory default, data traffic from netzone 1 to netzone 2 is blocked by the firewall.
However, data traffic can be realized in different zones with the following settings
- The firewall feature allows special permission or blocking of network access to individual or multiple network clients.
- The NAT function allows data exchange between netzones.
Port forwarding..
Port forwarding is a technique whereby data packets sent to an IP address and a specific device port can be forwarded to another destination IP address and another destination port in the network.
The original destination IP address and original destination port in the header of the incoming data packet are translated according to port forwarding rules.
The header translation is entered into the device’s Connection Tracking table. Response packets are compared to these entries and the header data is converted to the original values.
Note that the firewall automatically allows data traffic from the IP addresses and ports defined in the port forwarding rules.
Detailed Usage?
✓Remote monitoring and control
Industrial operations often require continuous monitoring of equipment, machinery, and processes, and Port Forwarding allows remote access to these systems, allowing operators to monitor and adjust parameters from remote locations.
For example, technicians can remotely access the control systems of manufacturing machinery via a secure connection to monitor performance and diagnose problems.
✓IoT Device Integration
Many industrial environments utilize IoT devices for data collection and automation. Port Forwarding allows these devices to communicate with a central server or control center via the Internet.
For example, sensors on the production line could use port forwarding for service accessibility and send data back to a central dashboard for analysis.
✓SCADA System
Supervisory Control and Data Acquisition (SCADA) systems often require remote access to monitor and control industrial processes, and port forwarding can make this access secure.
For example, engineers can remotely access SCADA systems to control pumps, valves, and alarms to ensure operational efficiency.
✓Maintenance and Support
Industrial equipment often requires regular maintenance and troubleshooting, and port forwarding allows support personnel and manufacturers to remotely connect to systems for diagnostics and repairs.
For example, service providers can access a machine’s control system to diagnose problems without having to visit in person, thus reducing downtime.
✓Data Sharing and Integration
Port forwarding enables the integration of different systems and databases within an industrial ecosystem and allows data to be transmitted seamlessly between applications.
For example, a manufacturing execution system (MES) and a warehouse management system (WMS) can be integrated to improve operational visibility and inventory management.
✓Remote Training
Staff training on equipment and software can be done remotely using port forwarding, allowing trainers to share access and demonstrate features without being on-site.
For example, this can be used to conduct online training sessions for employees with remote access to the system on how to use a new machine or software application.
Security Considerations
Incorporating port forwarding into industrial applications can increase efficiency, enable proactive maintenance, and improve operational flexibility, but it also poses security risks and requires addressing a variety of security measures.For example…
- Implement strong authentication and secure passwords
- Use a virtual private network (VPN) for secure remote connections
- Update connected systems and devices regularly
- Monitor network traffic for unauthorized access attempts
Start it!
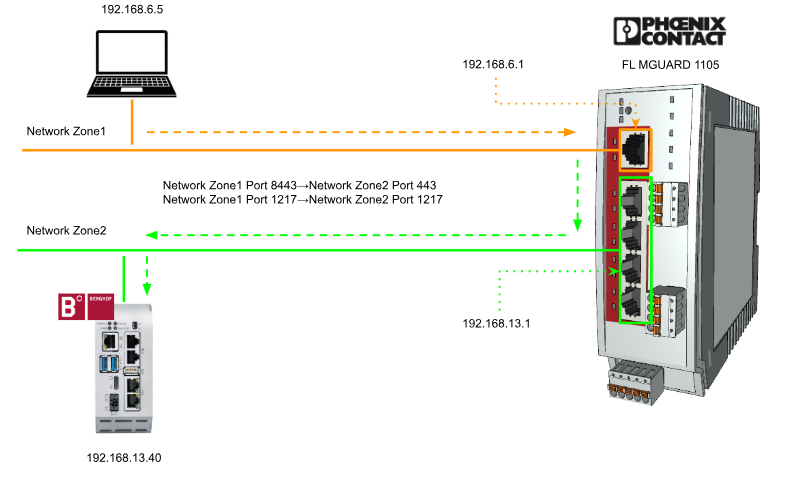
Now let’s set up the network configuration for Port Forwarding on Phoenix Contact’s Security Router FL MGUARD 1105.In the figure below, Network Zone 1 (OFFICE area) contains my PC and is connected to XF1 of FL MGUARD 1105.And in Network Zone2 (OT area), Berghof’s Raspberry Controller is located.
I will now access Berghof’s Raspberry Controller Web Server and Codesys Runtime on my own PC.
Configure Interface
The first step is to configure the Interface settings for network zones 1 and 2.
Access the FL MGUARD 1105 Web Server and configure Interfaces>Interfaces> Net zone1 and Net zone2 IP address settings and other settings to match your actual application.
Network Mode
This article will use the Port Forwarding function, so set Interfaces>Interfaces>Mode to Router.
We will be setting up Stealth mode in the future!
Configure Table
The next step is to add the Port Forwaring configuration table to FL MGUARD 1105.
Click on the NAT Tab to configure Port forwarding and 1:1 NAT.Here is a brief explanation of NAT settings.
IP Masquerade
One major function of Network Address Translation (NAT) is to hide the actual IP address of connected network clients from external network devices.
When a network client sends data through a device, the device replaces the source IP address (src_ip) with its own IP address (of the sending interface).
As the source IP address, the data recipient is always informed of the IP address of the mGuard device. It then sends a response packet to the mGuard device, which forwards it to the original sender (network client).
In this configuration, Net Zone 2 will be Masquerade, so set the Radio button for Zone 2 to On.
Next, you can add a route by clicking on the Port forwarding rule in the Add Row.
Done!
Protocol
Sets the network protocol used to send data packets so that the rule is applied (Default=TCP).
From
Set the net zones where data packets must be sent to the device so that the rules apply.
- From Net zone1=Data packets forwarded from Network Zone1 to Network Zone2
- From Net zone2=Data packets forwarded from Network Zone 2 to Network Zone 1
Incoming port
Set the device network port to which data packets need to be sent so that the rules apply.Data packets sent to this port will normally be forwarded to the specified destination IP address (To IP) and the defined destination port (To port).
- The destination IP address in the data packet header is translated to the destination IP address defined in the rule (To IP).
- The destination port in the data packet header is converted to the destination port (To port) defined in the rule.
Incoming port can be set from 1 to 65535. The following ports cannot be set because they are used for device services.
- dns (53)
- https (443)
- ntp (123)
- snmp (161)
- dhcp (67, 68)
To IP
Sets the IP address of the destination client to which incoming data packets are forwarded when the rule is applied.The original destination address in the header of the data packet can be translated to this IP address.
To Port
When the rule is applied, the network port to which incoming data packets are forwarded can be configured. The original destination port of the data packet header is translated to this port.
Result
This is the Port Forwarding set up in this article.
As shown in the figure below, data at 192.168.6.1:1217 is transferred to 192.168.13.40:1217.Also, the data in 192.168.6.1:8443 is transferred to 192.168.13.40:443.
Save
Finally, save your settings.
Result
Access 192.168.6.1:8443 with a web browser such as Chrome (i.e. the network interface of FL MGUARD 1105 XF1).
Done!I was able to access the Web Server of the BERGHOF Raspberry Controller.
Next, since we accessed Berghof’s Controller on the Codesys IDE, we do Communication Settings>Gateway> Add new Gateway.
Set IP-Address to the network Interface IP address of the FL MGUARD 1105 XF1.
Done!The next step is to configure the Gateway added earlier from the Drop-List.
Click Scan network.
You could search for Berghof’s Controller.
So the connection is Ok.
Of course, you can also download, upload, and monitor projects!