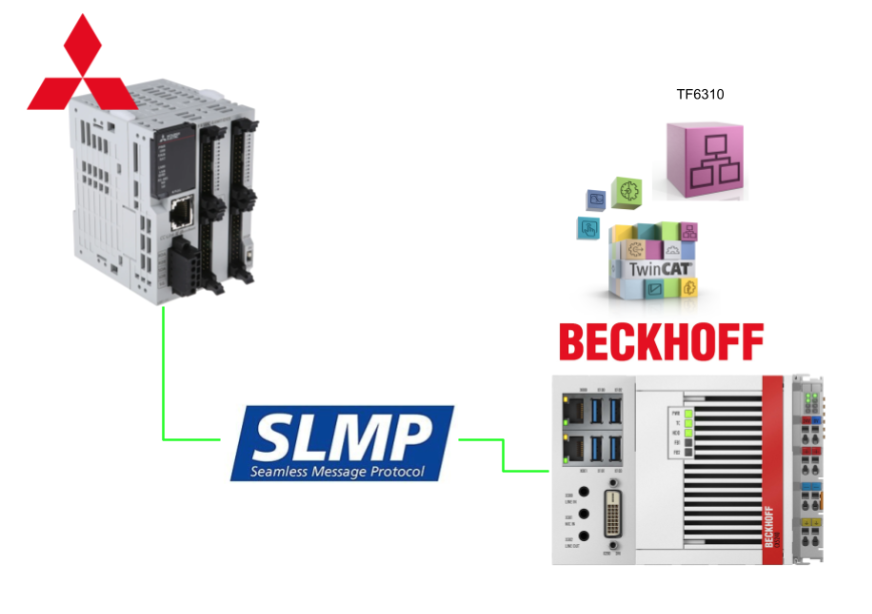
This article demonstrates how to use the TF6310 with Beckhoff TwinCAT3 to launch an SLMP Client and read/write data with Mitsubishi Electric’s FX5U PLC.
Right then, let’s enjoy the FA.
Reference Link
MC protocol
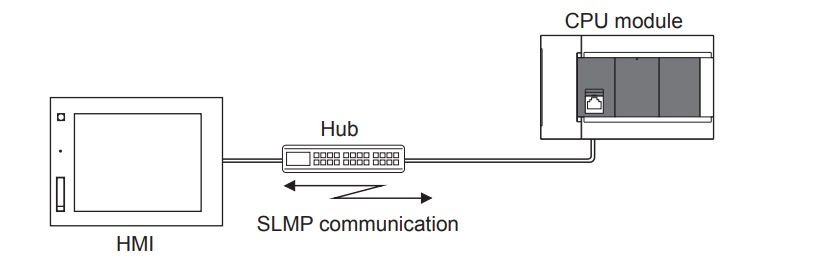
SLMP is a protocol for accessing SLMP-compliant devices via Ethernet from modules or external equipment (such as PCs or HMIs) equipped with Ethernet.
Between devices capable of SLMP communication, message transfer via SLMP is possible. The Ethernet port of the Ethernet module installed on the CPU can be used as an SLMP server.
Each SLMP is identical to the frames of the following MC protocol.
- 3E Frame: QnA-compatible 3E Frame for the MC Protocol
- 1E frame 1E frame compatible with the MC protocol
The external devices used with the above MC protocol can be connected to SLMP-compatible devices.
Functions
Server functions
Based on request messages (commands) from external devices, the CPU module performs data processing and data transfer.
Client functionality
Specialised commands enable the transmission of request messages to external devices and the reception of response messages from external devices.
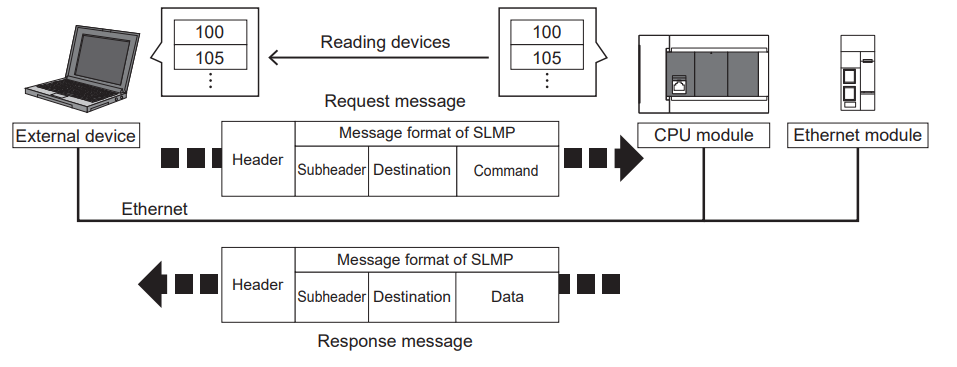
System monitoring from external devices (such as PCs, HMIs, etc.)
By sending request messages in SLMP message format from external devices to the Ethernet-equipped module, device read operations become possible, enabling system monitoring. Using SLMP not only allows reading device data but also enables writing device data and resetting the Ethernet-equipped module.
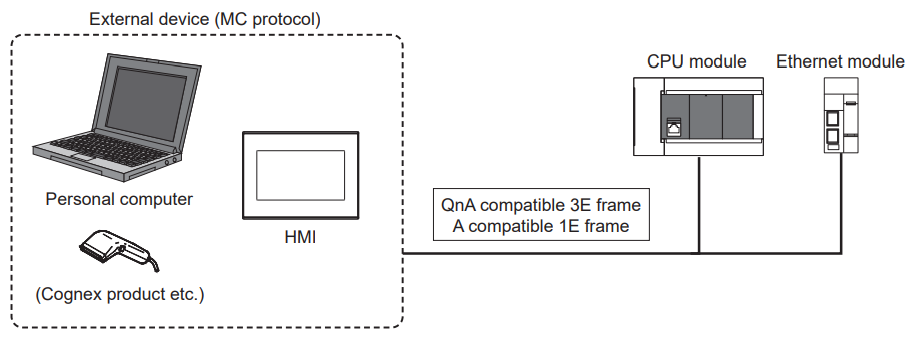
Connection to external devices used with the MC protocol
External devices utilising MC protocol QnA-compatible 3E frames and MC protocol A-compatible 1E frames can be connected directly to the Ethernet module.
Access via the network
SLMP enables external devices to access modules within the same network or other networks seamlessly via SLMP-compatible devices.
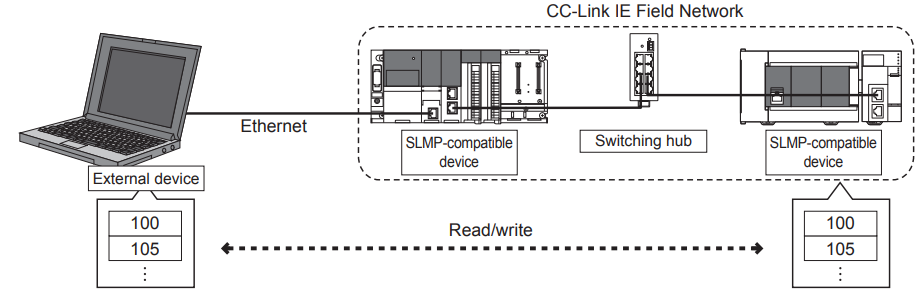
The Concept of SLMP
Now, let us examine the concept of the procedure (control procedure) for external devices to access the Ethernet-compatible module using SLMP.
Sending command messages
To access an Ethernet-equipped module, the SLMP communication must send the next command message only after receiving the response message from the Ethernet-equipped module for the previous command message. Note that the next command message cannot be sent until the response message has been fully received.
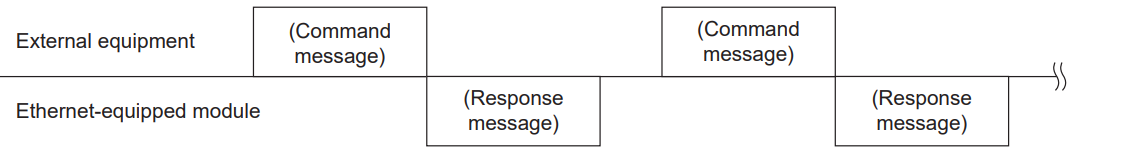
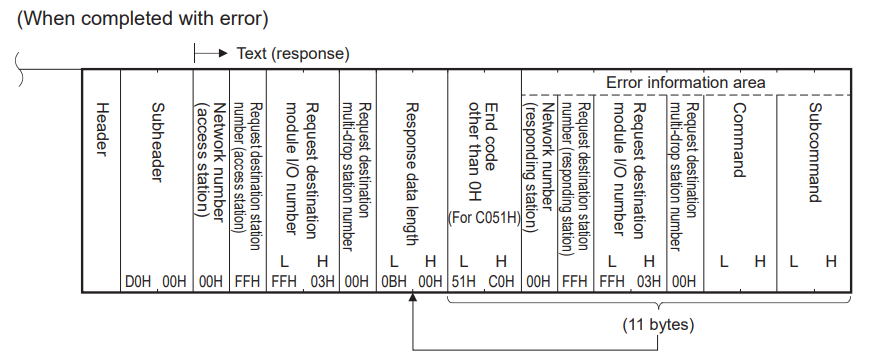
If the completion response message cannot be received
If you receive a completion response message containing an error, please handle it according to the error code within the response message.
Message format
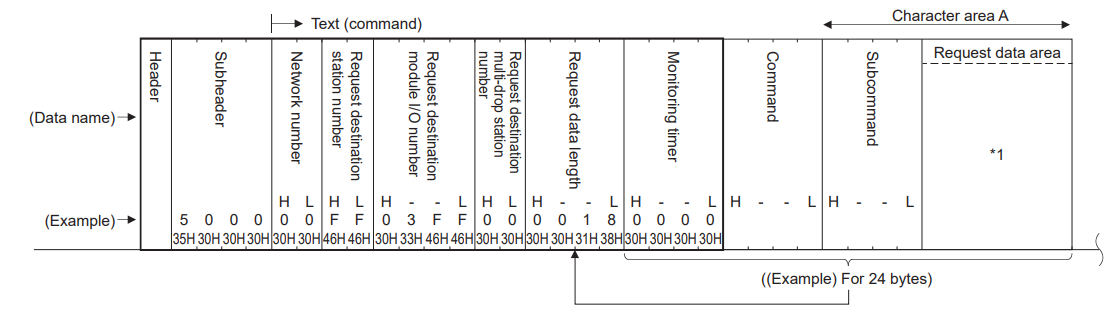
Moving forward, we shall examine the message data format and data specification methods for SLMP data communication using 3E frames over Ethernet ports.
Data format
The data format for communication between the built-in Ethernet port and external devices consists of a header and application data.
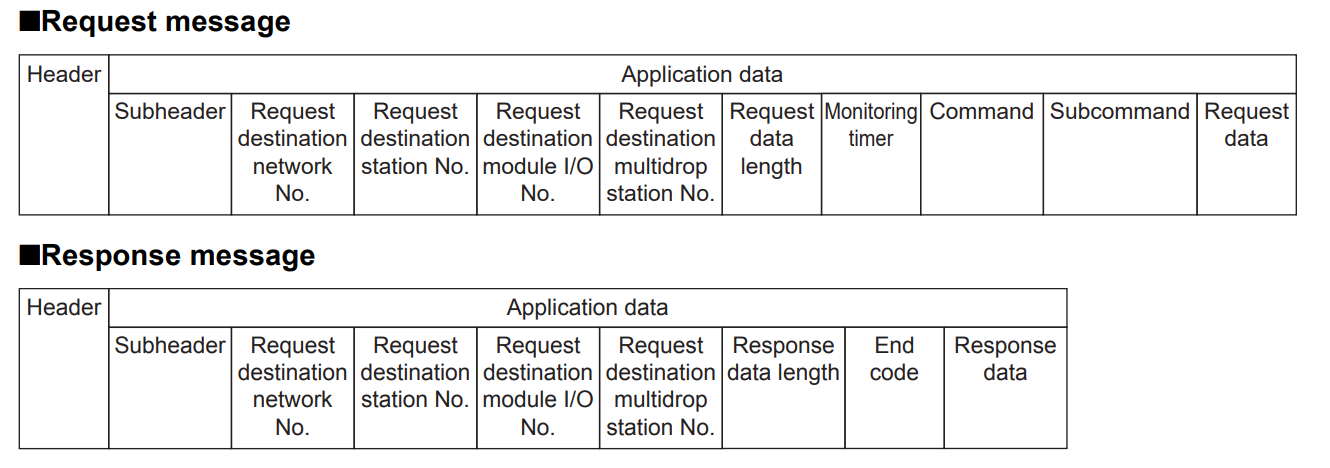
Header
This header is for TCP/IP and UDP/IP. Before sending a message, the header is automatically added by the external device’s Ethernet-compatible module (command message).
Application data
Application data is divided into subheaders and text. The subheader indicates whether the message is a command message or a response message. Furthermore, the text comprises the request data (command) and response data (response) for each function.
When communicating data using ASCII code
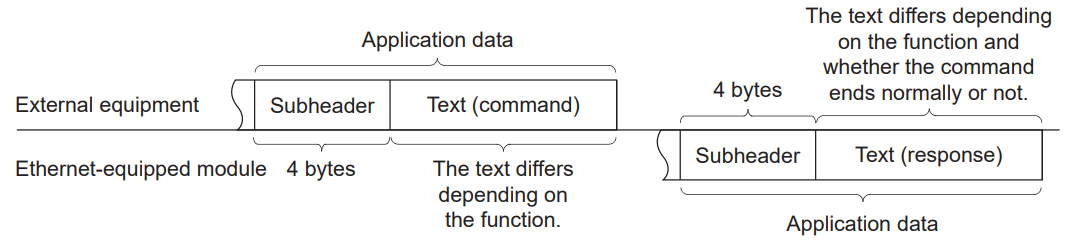
When transmitting data in binary code
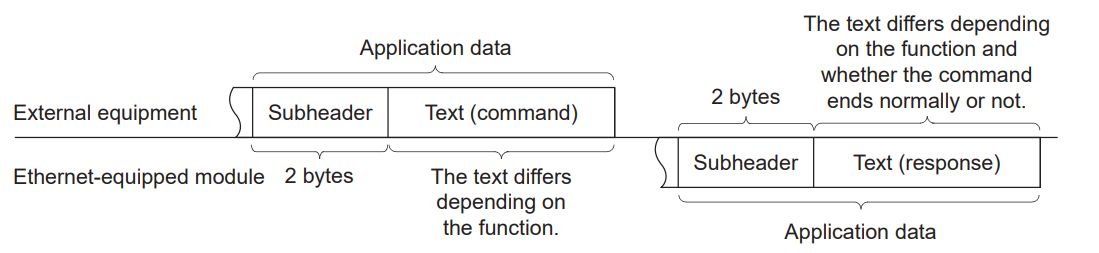
Subheader settings
This is the subheader configuration for the 3E Frame.
ASCIIコードでデータを通信する場合
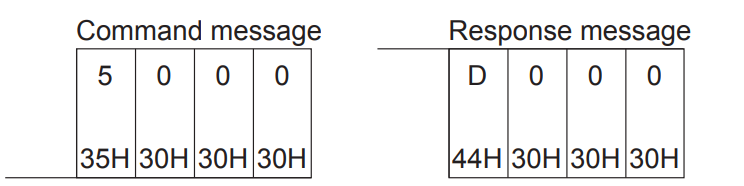
Binaryコードでデータを通信する場合
Control procedure
Let us now examine the control procedures for executing data communication and the format of application data.
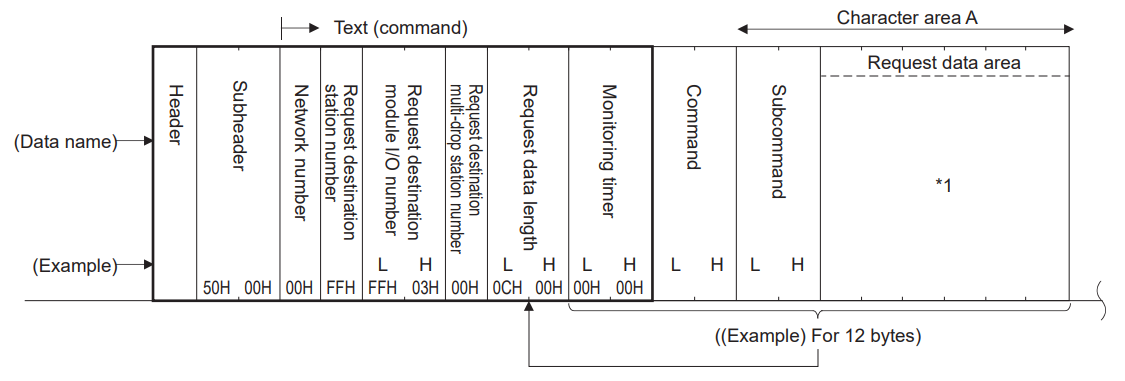
When transmitting data using ASCII code
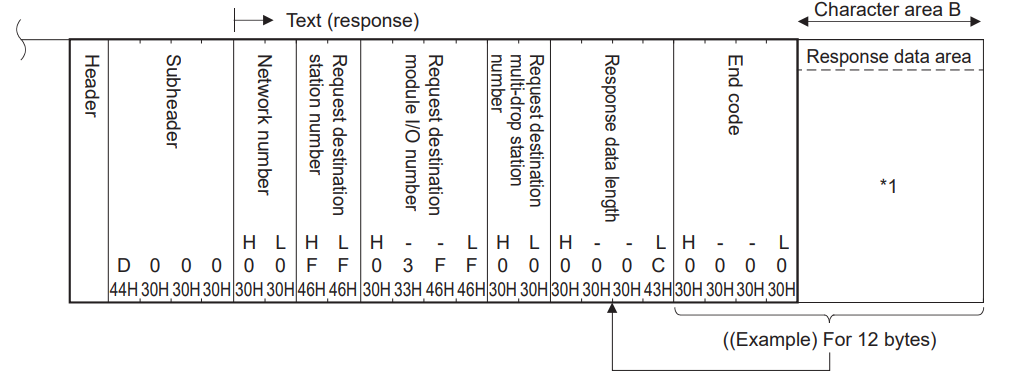
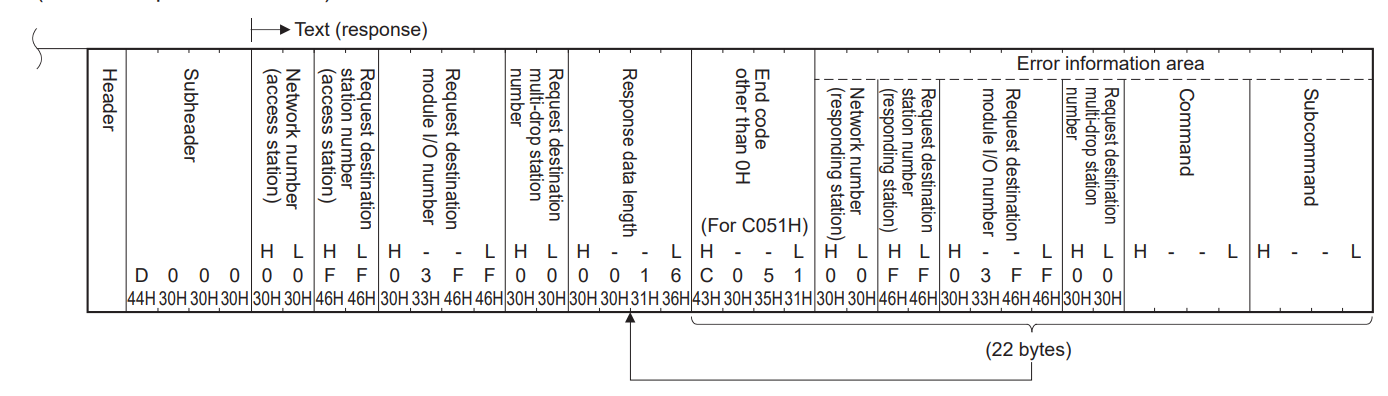
When transmitting data in binary code
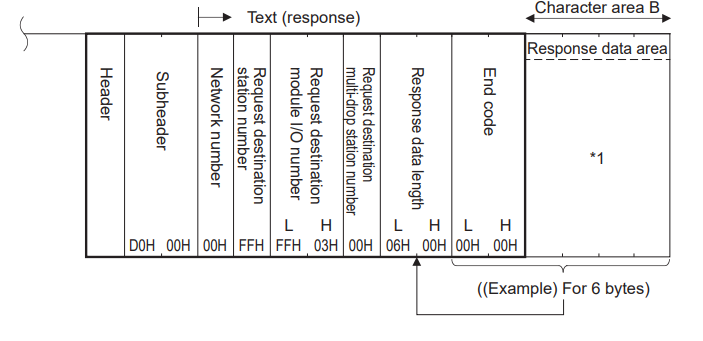
Reading and writing data
When reading or writing data to the device memory of the CPU module and the buffer memory of the intelligent function module, the following operations can be performed:
Reading data
Monitoring of CPU module operation, data analysis, and production control can be performed by external devices.
Writing data
The PLC writes data from external devices.
Batch Read and Write
This command enables the batch reading and writing of values from consecutive devices by specifying the number of device points.
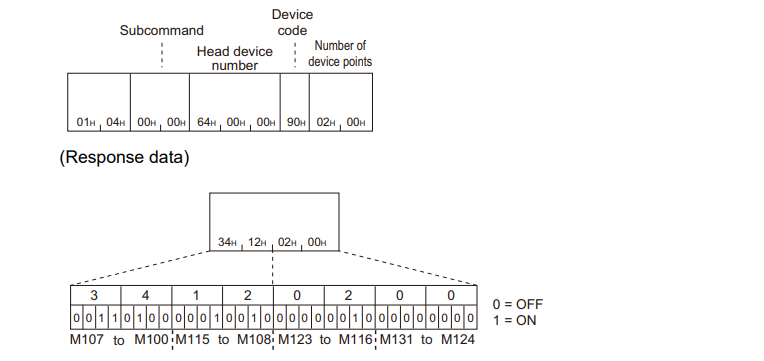
Batch read in word units (command: 0401)
This command reads values from the device on a word-by-word basis.

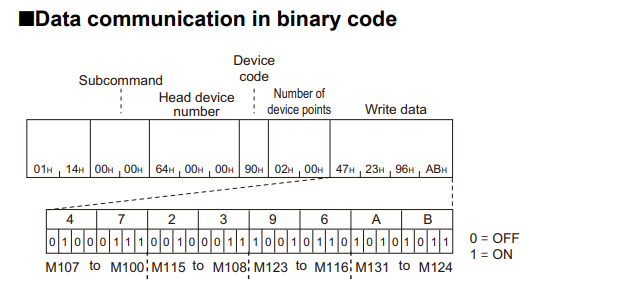
Batch write in word units (command: 1401)
This command writes values to the device on a word-by-word basis.

Protocols
The TCP protocol is a connection-oriented transport protocol (OSI Layer 4), functioning much like a telephone connection. Data streams (bytes) can be reliably transferred via TCP upon request.
The TCP protocol is used in networks where data sent from a client or server requires acknowledgement from the other party. The TCP protocol is suitable for transferring large volumes of data or data streams where start/end identifiers are not defined.
For the sender, this is not an issue as it knows how many bytes of data have been transmitted. However, the receiver cannot detect where a message ends and where the next data stream begins within the data stream.
TCP/IP Client
To implement a minimal TCP/IP client within the PLC, the following function blocks are required:
-
FB for establishing and terminating connections with remote servers
- FB_SocketConnect and FB_SocketClose instances
- Furthermore, FB_ClientServerConnection incorporates the functionality of both function blocks.
- An instance of the function block FB_SocketSend and/or FB_SocketReceive for exchanging data (sending and receiving) with a remote server.
TCP/IP server
To implement a minimal TCP/IP server within the PLC, the following function blocks are required:
- Open a listener socket using an instance of FB_SocketListen FB
- FB_SocketAccept and FB_SocketClose FB instances
- FB_ServerClientConnection combines the functionality of three function blocks.
To establish and terminate connections with remote clients:
- For data exchange (transmission and reception) with remote clients, use one instance of FB_SocketSend and/or FB_SocketReceive.
- Each PLC runtime system that opens a socket uses one instance of the FB FB_SocketCloseAll function block.
- Instances of FB_SocketAccept and FB_SocketReceive are called periodically (polled), while others are called as required.
Implementation
Right then, let’s get down to building the programme.
GXWORKS Side
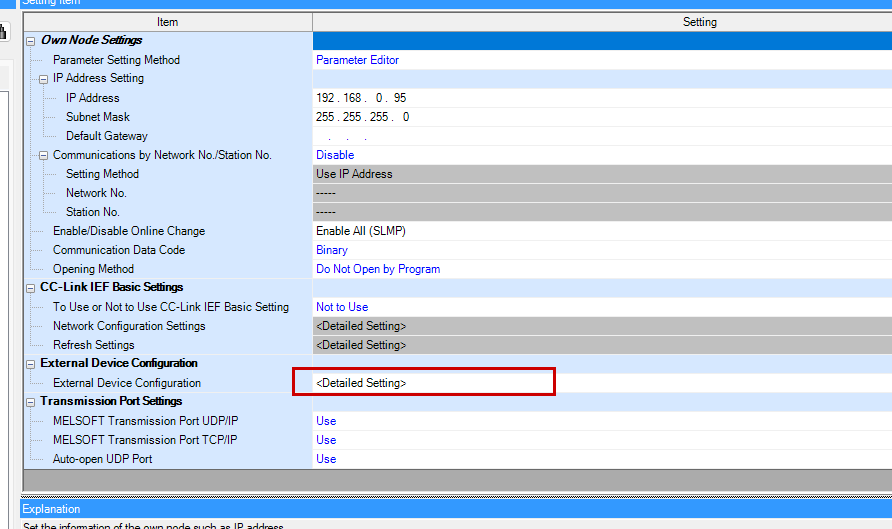
On the Mitsubishi IQ-R side, no basic programming is required; only configuration is needed. Click R00CPU → Module Parameter.
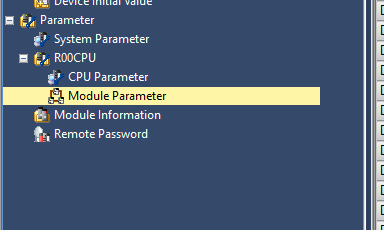
Configure the IP address to suit the application.
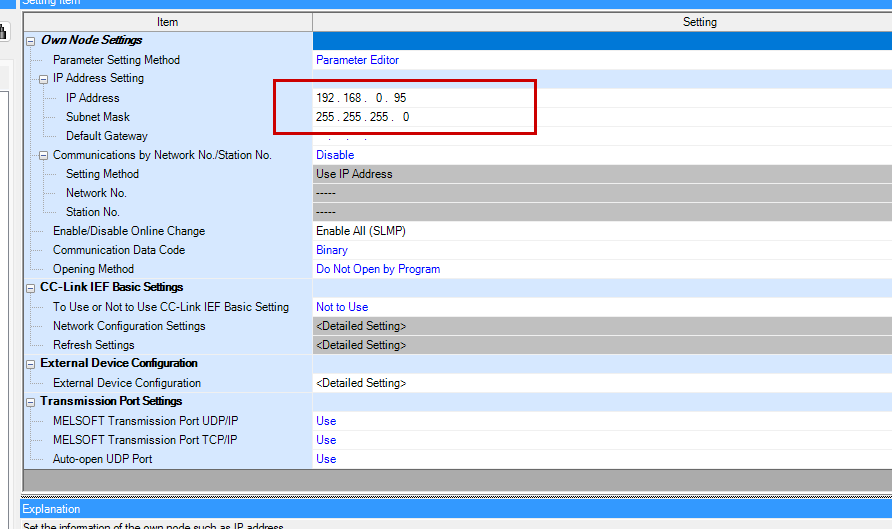
Set Enable/Disable Online Change to “Enable All (SLMP)”.
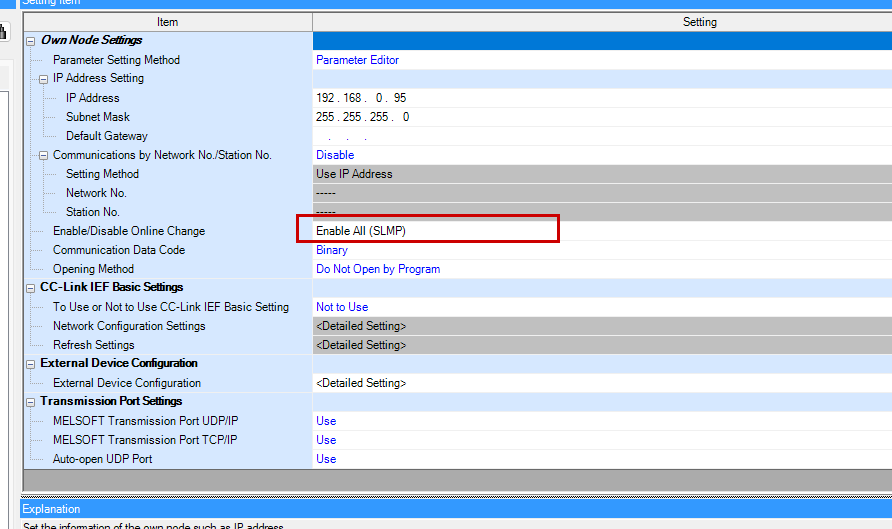
This time, as we are constructing the SLMP Protocol frame using byte data on the Beckhoff TwinCAT3 side, we shall set the Communication Data Code to “Binary”.
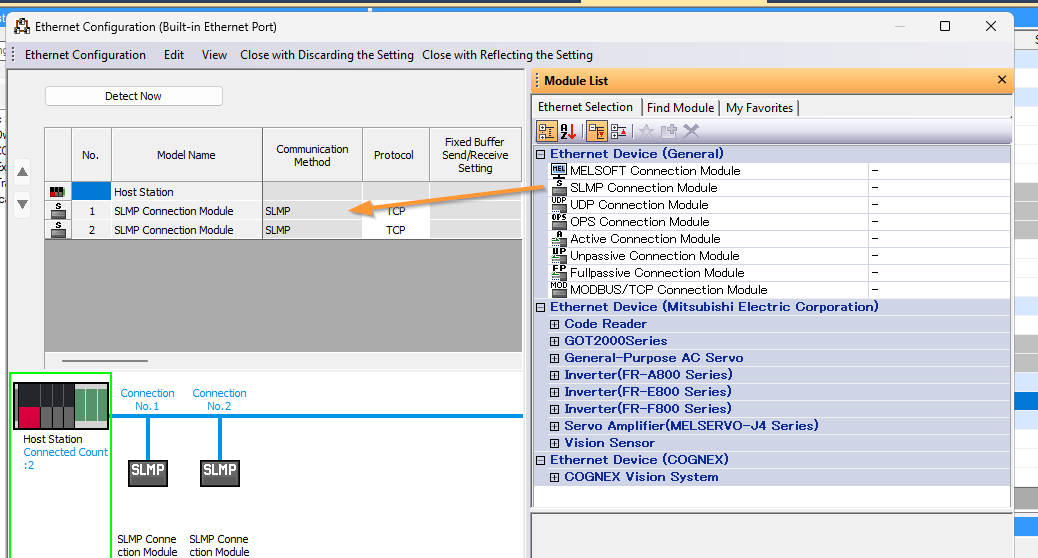
Next, we shall configure the SLMP Client connection port, so click on External Device Configuration.
Add an Ethernet Device→SLMP Connection Module. Finally, download the project to the Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC.
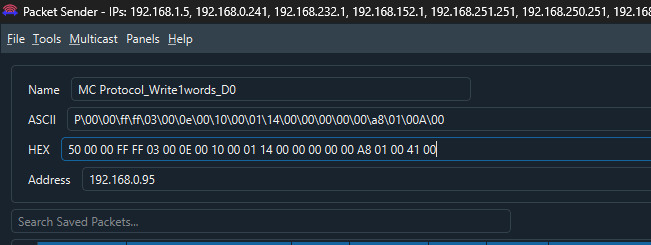
Test with Packet Sender
Before programming in TwinCAT, use the free Packet Sender tool to send SLMP Protocol messages to the Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC and verify communication.
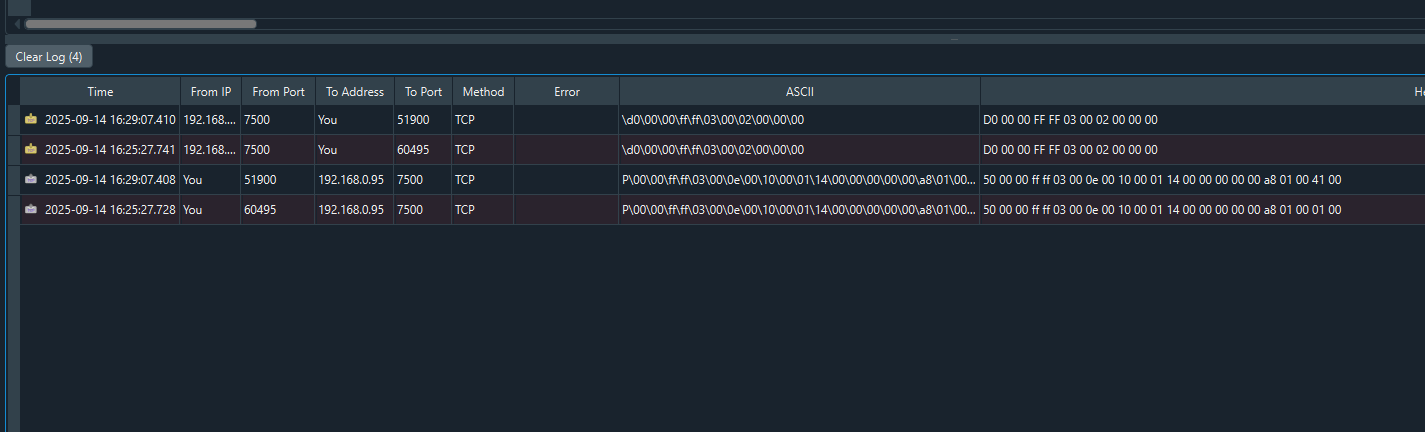
Done!A normal response has been received from the Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC.
Beckhoff TwinCAT3
TF6310
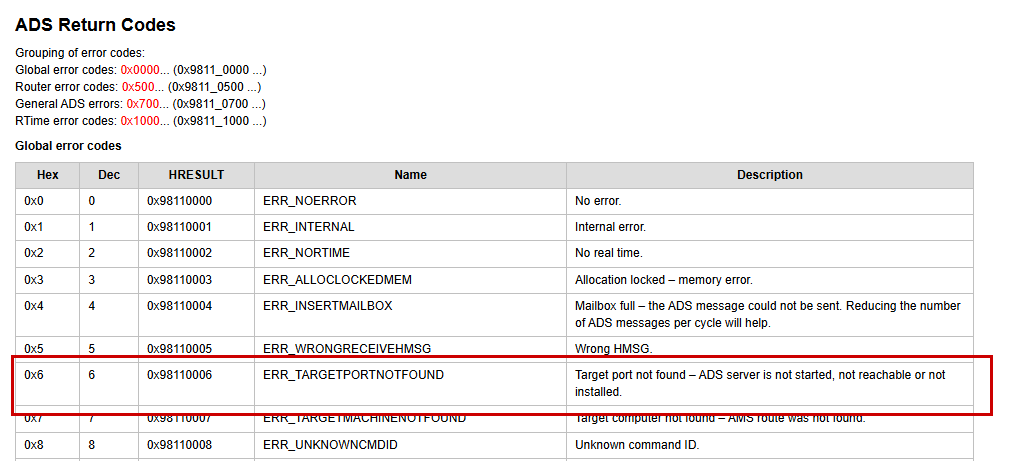
If an error code 0x06 occurs during socket communication, please verify that TF6310 has been installed in the TwinCAT environment where TF6310 is actually being implemented.
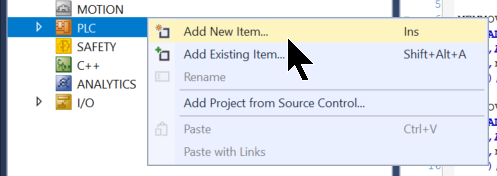
PLC
Add a PLC to the TwinCAT project.
ENUM
First, create an ENUM data type.
eMCProtocol
This ENUM is the code used when employing SLMP e3Frame.
{attribute ‘qualified_only’}
|
|---|
eMCProtocolDeviceCode
This ENUM is the code used when accessing each device via SLMP.
{attribute ‘qualified_only’}
|
|---|
FB
Next, we will create FB.
fbMCProtocolRead
This FB uses command 0401 to perform a bulk read of a specific memory area within the Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC.
VAR
This defines variables within fbMCProtocolRead and for the INPUT/OUTPUT parameters.
FUNCTION_BLOCK fbMCProtocolRead
|
|---|
Program
Next, we will create the programme.
- Step0 = Initialise FB and other components whilst awaiting xStart activation
- Step10=Connect to Mitsubishi IQ-R. If connection succeeds, proceed to Step=20; if it fails, proceed to Step=990.
- Step 20: Frame Creation for the MC Protocol
- Step 30: Send Frame to Mitsubishi IQ-R. If transmission succeeds, proceed to Step 35; if it fails, proceed to Step 991.
- Step35=Wait for Mitsubishi IQ-R’s response. If received, proceed to Step40.
- Step40=Wait for OFF signal to execute received feedback
- Step 50 = If the data is received and is normal, then Step = 60; if there is an error, then Step = 992
- Step60=Output the received data, then return to Step20
- Step100=Disconnect TCP connection with Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC
- Step299=Reset Step to 0
- Step990, Step991, Step992 = Error handling
fbRTrig(CLK:=xStart);
|
|---|
fbMCProtocolWrite
This FB uses command 1401 to perform a bulk write to a specific area of memory within the Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC.
VAR
This defines variables within fbMCProtocolWrite and for the INPUT/OUTPUT parameters.
FUNCTION_BLOCK fbMCProtocolWrite
|
|---|
Program
Next, we will create the programme.
- Step0 = Initialise FB and other components, and await xStart activation
- Step10=Connect to Mitsubishi IQ-R. If connection succeeds, proceed to Step=20; if it fails, proceed to Step=990.
- Step 20: Frame Creation for the MC Protocol
- Step 30: Send Frame to Mitsubishi IQ-R. If transmission succeeds, proceed to Step 35; if it fails, proceed to Step 991.
- Step35=Wait for Mitsubishi IQ-R’s response. If received, proceed to Step40.
- Step40=Wait for OFF signal to execute received feedback
- Step 50 = If the data is received and is normal, then Step = 60; if there is an error, then Step = 992
- Step 60 = Step 20 Back
- Step100=Disconnect TCP connection with Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC
- Step299=Reset Step to 0
- Step990, Step991, Step992 = Error handling
fbRTrig(CLK:=xStart);
|
|---|
MAIN
Finally, the MAIN programme.
VAR
Then we can declare the FB created earlier.
PROGRAM MAIN
|
|---|
Program
Then, simply configure the Mitsubishi IQ-R PLC’s IP address, port, and the device type, starting address, and number to be accessed.
fbMCProtocolRead(
|
|---|
Result
You can verify the operation from this video.
Donwload
Please download the project from this link.
https://github.com/soup01Threes/TwinCAT3/blob/main/TwinCAT-TestingWithMCProtocol.tnzip